Duplicate Key Model
The Duplicate Key Model in Doris is the default table model, designed to store individual raw data records. The Duplicate Key specified during table creation determines the columns for sorting and storage, optimizing common queries. It is recommended to choose no more than three columns as the sort key. For more specific selection guidelines, refer to Sort Key. The Duplicate Key Model has the following characteristics:
-
Preserving Raw Data: The Duplicate Key Model retains all original data, making it ideal for storing and querying raw data. It is recommended for use cases requiring detailed data analysis to avoid data loss.
-
No Deduplication or Aggregation: Unlike the Aggregate and Primary Key models, the Duplicate Key Model does not perform deduplication or aggregation, fully retaining identical records.
-
Flexible Data Querying: The Duplicate Key Model retains all original data, enabling detailed extraction and aggregation across any dimension for metadata auditing and fine-grained analysis.
Use Cases
In the Duplicate Key Model, data is generally only appended, and old data is not updated. The Duplicate Key Model is ideal for scenarios that require full raw data:
-
Log Storage: Used for storing various types of application logs, such as access logs, error logs, etc. Each piece of data needs to be detailed for future auditing and analysis.
-
User Behavior Data: When analyzing user behavior, such as click data or user access paths, it is necessary to retain detailed user actions. This helps in building user profiles and conducting detailed analysis of behavior patterns.
-
Transaction Data: For storing transaction or order data, once a transaction is completed, there is typically no need for data changes...
Table Creation Instructions
When creating a table, the DUPLICATE KEY keyword can be used to specify the Duplicate Key Model. The Duplicate Key table must specify the Key columns, which are used to sort the data during storage. In the following example, the Duplicate Key table stores log information and sorts the data based on the log_time, log_type, and error_code columns:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS example_tbl_duplicate
(
log_time DATETIME NOT NULL,
log_type INT NOT NULL,
error_code INT,
error_msg VARCHAR(1024),
op_id BIGINT,
op_time DATETIME
)
DUPLICATE KEY(log_time, log_type, error_code)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(log_type) BUCKETS 10;
Data Insertion and Storage
In a Duplicate Key table, data is not deduplicated or aggregated; inserting data directly stores it. The Key columns in the Duplicate Key Model are used for sorting.
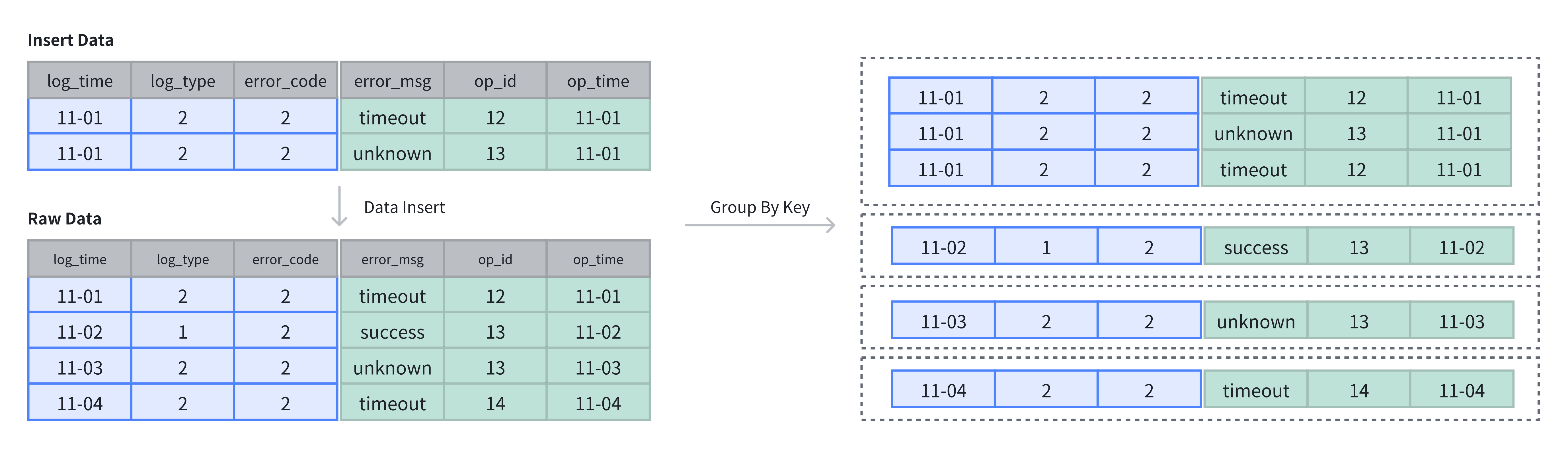
In the example above, after inserting 2 rows into the initial 4 rows, the data is appended, resulting in a total of 6 rows.
-- 4 rows raw data
INSERT INTO example_tbl_duplicate VALUES
('2024-11-01 00:00:00', 2, 2, 'timeout', 12, '2024-11-01 01:00:00'),
('2024-11-02 00:00:00', 1, 2, 'success', 13, '2024-11-02 01:00:00'),
('2024-11-03 00:00:00', 2, 2, 'unknown', 13, '2024-11-03 01:00:00'),
('2024-11-04 00:00:00', 2, 2, 'unknown', 12, '2024-11-04 01:00:00');
-- insert into 2 rows
INSERT INTO example_tbl_duplicate VALUES
('2024-11-01 00:00:00', 2, 2, 'timeout', 12, '2024-11-01 01:00:00'),
('2024-11-01 00:00:00', 2, 2, 'unknown', 13, '2024-11-01 01:00:00');
-- check the rows of table
SELECT * FROM example_tbl_duplicate;
+---------------------+----------+------------+-----------+-------+---------------------+
| log_time | log_type | error_code | error_msg | op_id | op_time |
+---------------------+----------+------------+-----------+-------+---------------------+
| 2024-11-02 00:00:00 | 1 | 2 | success | 13 | 2024-11-02 01:00:00 |
| 2024-11-01 00:00:00 | 2 | 2 | timeout | 12 | 2024-11-01 01:00:00 |
| 2024-11-03 00:00:00 | 2 | 2 | unknown | 13 | 2024-11-03 01:00:00 |
| 2024-11-04 00:00:00 | 2 | 2 | unknown | 12 | 2024-11-04 01:00:00 |
| 2024-11-01 00:00:00 | 2 | 2 | unknown | 13 | 2024-11-01 01:00:00 |
| 2024-11-01 00:00:00 | 2 | 2 | timeout | 12 | 2024-11-01 01:00:00 |
+---------------------+----------+------------+-----------+-------+---------------------+

