Routine Load
Doris can continuously consume data from Kafka Topics through Routine Load. After submitting a Routine Load job, Doris will keep the import job running, continuously generating import tasks to consume messages from specified Topics in the Kafka cluster.
Routine Load is a streaming import job that supports Exactly-Once semantics, ensuring no data loss or duplication.
Use Cases
Supported Data Sources
Routine Load supports consuming data from Kafka clusters.
Supported Data File Formats
Routine Load supports CSV and JSON format data.
When importing CSV format, you need to clearly distinguish between null values and empty strings:
-
Null values need to be represented by
\n. The dataa,\n,bindicates that the middle column is a null value. -
Empty strings ('') are directly left empty. The data
a,,bindicates that the middle column is an empty string.
Usage Limitations
When using Routine Load to consume data from Kafka, there are the following limitations:
-
Supported message formats are CSV and JSON text formats. Each CSV message is one line, and the line does not include a line break at the end.
-
By default, Kafka version 0.10.0.0 (inclusive) and above are supported. To use versions below Kafka 0.10.0.0 (0.9.0, 0.8.2, 0.8.1, 0.8.0), you need to modify the BE configuration by setting the value of
kafka_broker_version_fallbackto the compatible older version, or directly set the value ofproperty.broker.version.fallbackwhen creating Routine Load to the compatible older version. The cost of using older versions is that some new features of Routine Load may not be available, such as setting Kafka partition offsets based on time.
Basic Principles
Routine Load continuously consumes data from Kafka Topics and writes it into Doris.
In Doris, after creating a Routine Load job, a persistent import job is generated, including several import tasks:
-
Import Job (Load Job): A Routine Load Job is a persistent import job that continuously consumes data from the data source.
-
Import Task (Load Task): An import job is divided into several import tasks for actual consumption. Each task is an independent transaction.
The specific process of Routine Load import is shown in the following diagram:
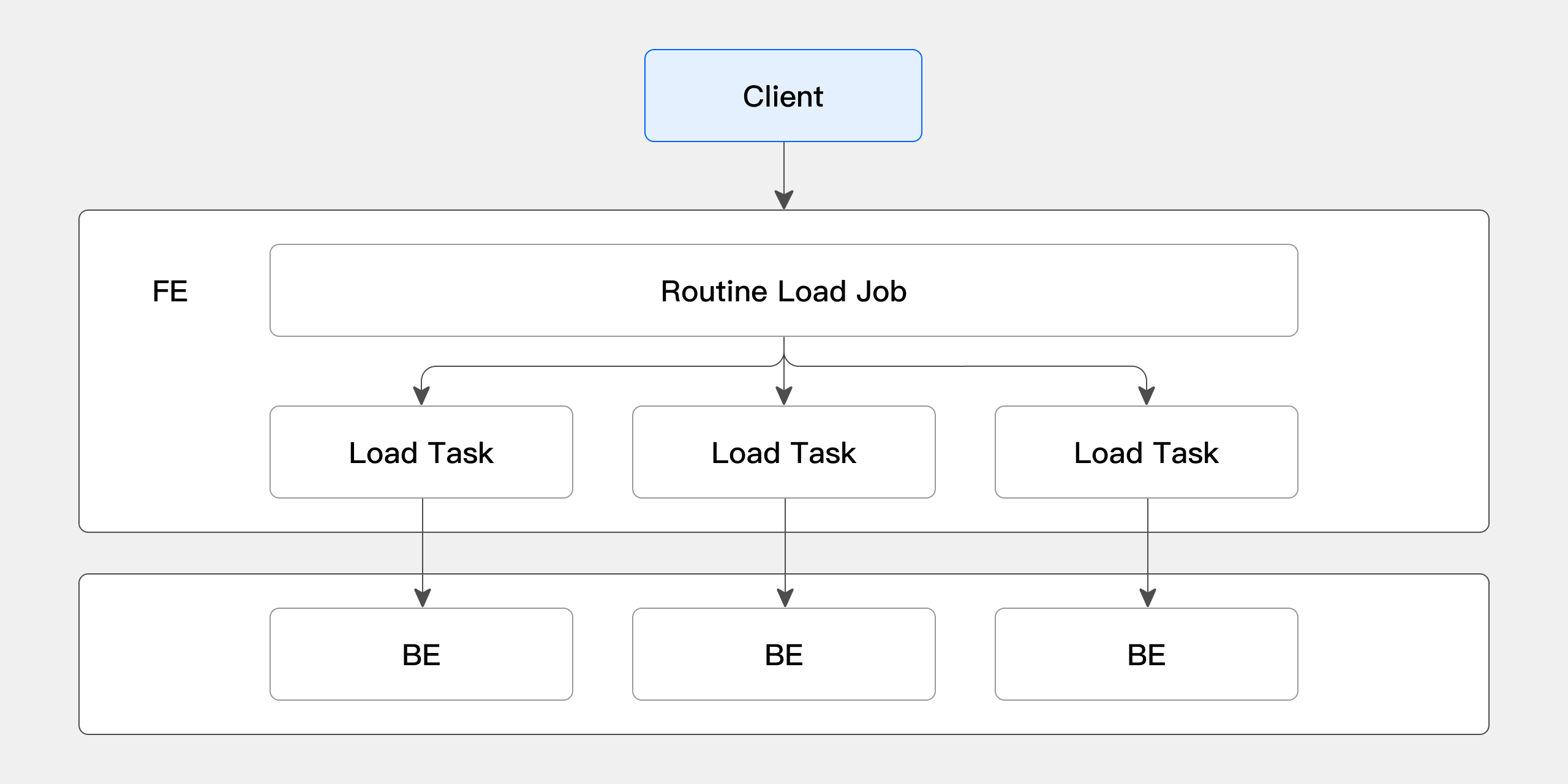
-
Client submits a request to FE to create a Routine Load job. FE generates a persistent import job (Routine Load Job) through the Routine Load Manager.
-
FE splits the Routine Load Job into several Routine Load Tasks through the Job Scheduler, which are scheduled by the Task Scheduler and dispatched to BE nodes.
-
On the BE, after a Routine Load Task completes import, it submits the transaction to FE and updates the Job metadata.
-
After a Routine Load Task is submitted, new Tasks are generated or timed-out Tasks are retried.
-
The newly generated Routine Load Tasks continue to be scheduled by the Task Scheduler in a continuous cycle.
Automatic Recovery
To ensure high availability of jobs, an automatic recovery mechanism is introduced. In the case of unexpected pauses, the Routine Load Scheduler thread will attempt to automatically recover the job. For unexpected Kafka failures or other non-working situations, the automatic recovery mechanism can ensure that after Kafka recovers, the import job can continue to run normally without manual intervention.
Cases that will not automatically recover:
-
User manually executes the
PAUSE ROUTINE LOADcommand. -
Data quality issues exist.
-
Cases that cannot automatically recover, such as database tables being deleted.
Except for the above three cases, other paused jobs will attempt automatic recovery.
Quick Start
Create Import Job
In Doris, you can create a persistent Routine Load import task using the CREATE ROUTINE LOAD command. For detailed syntax, refer to CREATE ROUTINE LOAD. Routine Load can consume CSV and JSON data.
Import CSV Data
- Sample import data
In Kafka, there is the following sample data:
kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic test-routine-load-csv --from-beginning
1,Emily,25
2,Benjamin,35
3,Olivia,28
4,Alexander,60
5,Ava,17
6,William,69
7,Sophia,32
8,James,64
9,Emma,37
10,Liam,64
- Create the table to be imported
In Doris, create the table to be imported with the following syntax:
CREATE TABLE testdb.test_routineload_tbl(
user_id BIGINT NOT NULL COMMENT "user id",
name VARCHAR(20) COMMENT "name",
age INT COMMENT "age"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(user_id)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(user_id) BUCKETS 10;
- Create Routine Load import job
In Doris, use the CREATE ROUTINE LOAD command to create an import job:
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD testdb.example_routine_load_csv ON test_routineload_tbl
COLUMNS TERMINATED BY ",",
COLUMNS(user_id, name, age)
FROM KAFKA(
"kafka_broker_list" = "192.168.88.62:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "test-routine-load-csv",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
);
Import JSON Data
- Sample import data
In Kafka, there is the following sample data:
kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic test-routine-load-json --from-beginning
{"user_id":1,"name":"Emily","age":25}
{"user_id":2,"name":"Benjamin","age":35}
{"user_id":3,"name":"Olivia","age":28}
{"user_id":4,"name":"Alexander","age":60}
{"user_id":5,"name":"Ava","age":17}
{"user_id":6,"name":"William","age":69}
{"user_id":7,"name":"Sophia","age":32}
{"user_id":8,"name":"James","age":64}
{"user_id":9,"name":"Emma","age":37}
{"user_id":10,"name":"Liam","age":64}
- Create the table to be imported
In Doris, create the table to be imported with the following syntax:
CREATE TABLE testdb.test_routineload_tbl(
user_id BIGINT NOT NULL COMMENT "user id",
name VARCHAR(20) COMMENT "name",
age INT COMMENT "age"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(user_id)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(user_id) BUCKETS 10;
- Create Routine Load import job
In Doris, use the CREATE ROUTINE LOAD command to create an import job:
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD testdb.example_routine_load_json ON test_routineload_tbl
COLUMNS(user_id,name,age)
PROPERTIES(
"format"="json",
"jsonpaths"="[\"$.user_id\",\"$.name\",\"$.age\"]"
)
FROM KAFKA(
"kafka_broker_list" = "192.168.88.62:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "test-routine-load-json",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
);
If you need to import JSON objects from the root node of a JSON file, jsonpaths needs to be specified as $., for example: PROPERTIES("jsonpaths"="$.").
View Import Status
In Doris, the import job status and import task status of Routine Load:
-
Import Job: Mainly used to view the target table of the import task, number of subtasks, import delay status, import configuration, and import results.
-
Import Task: Mainly used to view the status of import subtasks, consumption progress, and dispatched BE nodes.
01 View Running Import Jobs
You can view import job status using the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD command. SHOW ROUTINE LOAD describes the basic status of the current job, such as the import target table, import delay status, import configuration information, and import error information.
For example, you can view the job status of testdb.example_routine_load_csv with the following command:
mysql> SHOW ROUTINE LOAD FOR testdb.example_routine_load\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Id: 12025
Name: example_routine_load
CreateTime: 2024-01-15 08:12:42
PauseTime: NULL
EndTime: NULL
DbName: default_cluster:testdb
TableName: test_routineload_tbl
IsMultiTable: false
State: RUNNING
DataSourceType: KAFKA
CurrentTaskNum: 1
JobProperties: {"max_batch_rows":"200000","timezone":"America/New_York","send_batch_parallelism":"1","load_to_single_tablet":"false","column_separator":"','","line_delimiter":"\n","current_concurrent_number":"1","delete":"*","partial_columns":"false","merge_type":"APPEND","exec_mem_limit":"2147483648","strict_mode":"false","jsonpaths":"","max_batch_interval":"10","max_batch_size":"104857600","fuzzy_parse":"false","partitions":"*","columnToColumnExpr":"user_id,name,age","whereExpr":"*","desired_concurrent_number":"5","precedingFilter":"*","format":"csv","max_error_number":"0","max_filter_ratio":"1.0","json_root":"","strip_outer_array":"false","num_as_string":"false"}
DataSourceProperties: {"topic":"test-topic","currentKafkaPartitions":"0","brokerList":"192.168.88.62:9092"}
CustomProperties: {"kafka_default_offsets":"OFFSET_BEGINNING","group.id":"example_routine_load_73daf600-884e-46c0-a02b-4e49fdf3b4dc"}
Statistic: {"receivedBytes":28,"runningTxns":[],"errorRows":0,"committedTaskNum":3,"loadedRows":3,"loadRowsRate":0,"abortedTaskNum":0,"errorRowsAfterResumed":0,"totalRows":3,"unselectedRows":0,"receivedBytesRate":0,"taskExecuteTimeMs":30069}
Progress: {"0":"2"}
Lag: {"0":0}
ReasonOfStateChanged:
ErrorLogUrls:
OtherMsg:
User: root
Comment:
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
02 View Running Import Tasks
You can view import subtask status using the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD TASK command. SHOW ROUTINE LOAD TASK describes the subtask information under the current job, such as subtask status, dispatched BE id, etc.
For example, you can view the task status of testdb.example_routine_load_csv with the following command:
mysql> SHOW ROUTINE LOAD TASK WHERE jobname = 'example_routine_load_csv';
+-----------------------------------+-------+-----------+-------+---------------------+---------------------+---------+-------+----------------------+
| TaskId | TxnId | TxnStatus | JobId | CreateTime | ExecuteStartTime | Timeout | BeId | DataSourceProperties |
+-----------------------------------+-------+-----------+-------+---------------------+---------------------+---------+-------+----------------------+
| 8cf47e6a68ed4da3-8f45b431db50e466 | 195 | PREPARE | 12177 | 2024-01-15 12:20:41 | 2024-01-15 12:21:01 | 20 | 10429 | {"4":1231,"9":2603} |
| f2d4525c54074aa2-b6478cf8daaeb393 | 196 | PREPARE | 12177 | 2024-01-15 12:20:41 | 2024-01-15 12:21:01 | 20 | 12109 | {"1":1225,"6":1216} |
| cb870f1553864250-975279875a25fab6 | -1 | NULL | 12177 | 2024-01-15 12:20:52 | NULL | 20 | -1 | {"2":7234,"7":4865} |
| 68771fd8a1824637-90a9dac2a7a0075e | -1 | NULL | 12177 | 2024-01-15 12:20:52 | NULL | 20 | -1 | {"3":1769,"8":2982} |
| 77112dfea5e54b0a-a10eab3d5b19e565 | 197 | PREPARE | 12177 | 2024-01-15 12:21:02 | 2024-01-15 12:21:02 | 20 | 12098 | {"0":3000,"5":2622} |
+-----------------------------------+-------+-----------+-------+---------------------+---------------------+---------+-------+----------------------+
Pause Import Job
You can pause an import job using the PAUSE ROUTINE LOAD command. After pausing the import job, it enters the PAUSED state, but the import job is not terminated and can be restarted using the RESUME ROUTINE LOAD command.
For example, you can pause the testdb.example_routine_load_csv import job with the following command:
PAUSE ROUTINE LOAD FOR testdb.example_routine_load_csv;
Resume Import Job
You can resume an import job using the RESUME ROUTINE LOAD command.
For example, you can resume the testdb.example_routine_load_csv import job with the following command:
RESUME ROUTINE LOAD FOR testdb.example_routine_load_csv;
Modify Import Job
You can modify a created import job using the ALTER ROUTINE LOAD command. Before modifying the import job, you need to pause it using PAUSE ROUTINE LOAD, and after modification, resume it using RESUME ROUTINE LOAD.
For example, you can modify the desired import task concurrency parameter desired_concurrent_number and modify Kafka Topic information with the following command:
ALTER ROUTINE LOAD FOR testdb.example_routine_load_csv
PROPERTIES(
"desired_concurrent_number" = "3"
)
FROM KAFKA(
"kafka_broker_list" = "192.168.88.60:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "test-topic"
);
Cancel Import Job
You can stop and delete a Routine Load import job using the STOP ROUTINE LOAD command. Deleted import jobs cannot be recovered and cannot be viewed through the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD command.
You can stop and delete the import job testdb.example_routine_load_csv with the following command:
STOP ROUTINE LOAD FOR testdb.example_routine_load_csv;
Bind Compute Group
In storage-compute separation mode, the Compute Group selection logic for Routine Load is as follows in order of priority:
- Select the Compute Group specified by the
use db@clusterstatement. - Select the Compute Group specified by the user attribute
default_compute_group. - Select one from the Compute Groups that the current user has permission to access.
In storage-compute integration mode, select the Compute Group specified in the user attribute resource_tags.location. If not specified in the user attribute, use the Compute Group named default.
Note that the Compute Group for a Routine Load job can only be specified at creation time. Once a Routine Load job is created, its bound Compute Group cannot be modified.
Reference Manual
Import Commands
The syntax for creating a Routine Load persistent import job is as follows:
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD [<db_name>.]<job_name> [ON <tbl_name>]
[merge_type]
[load_properties]
[job_properties]
FROM KAFKA [data_source_properties]
[COMMENT "<comment>"]
Module descriptions for creating import jobs:
| Module | Description |
|---|---|
| db_name | Specifies the database for creating the import task. |
| job_name | Specifies the name of the import task to be created. The same database cannot have tasks with the same name. |
| tbl_name | Specifies the name of the table to be imported. This is optional. If not specified, dynamic table mode is used, where Kafka data needs to contain table name information. |
| merge_type | Data merge type. Default is APPEND. merge_type has three options: - APPEND: Append import mode; - MERGE: Merge import mode; - DELETE: All imported data is to be deleted. |
| load_properties | Import description module, including the following components: - column_separator clause - columns_mapping clause - preceding_filter clause - where_predicates clause - partitions clause - delete_on clause - order_by clause |
| job_properties | Used to specify general import parameters for Routine Load. |
| data_source_properties | Used to describe Kafka data source properties. |
| comment | Used to describe remarks for the import job. |
Import Parameter Description
01 FE Configuration Parameters
| Parameter Name | Default Value | Dynamic Configuration | FE Master Exclusive Configuration | Parameter Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| max_routine_load_task_concurrent_num | 256 | Yes | Yes | Limits the maximum number of concurrent Routine Load import job subtasks. It's recommended to maintain the default value. Setting it too large may lead to too many concurrent tasks, occupying cluster resources. |
| max_routine_load_task_num_per_be | 1024 | Yes | Yes | Maximum number of concurrent Routine Load tasks limited per BE. max_routine_load_task_num_per_be should be less than routine_load_thread_pool_size. |
| max_routine_load_job_num | 100 | Yes | Yes | Limits the maximum number of Routine Load jobs, including NEED_SCHEDULED, RUNNING, PAUSE. |
| max_tolerable_backend_down_num | 0 | Yes | Yes | As long as one BE is down, Routine Load cannot automatically recover. Under certain conditions, Doris can reschedule PAUSED tasks to RUNNING state. A value of 0 for this parameter means rescheduling is only allowed when all BE nodes are alive. |
| period_of_auto_resume_min | 5 (minutes) | Yes | Yes | The period for automatic recovery of Routine Load. |
02 BE Configuration Parameters
| Parameter Name | Default Value | Dynamic Configuration | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| max_consumer_num_per_group | 3 | Yes | Maximum number of consumers a subtask can generate for consumption. |
03 Import Configuration Parameters
When creating a Routine Load job, you can specify different import configuration parameters for different modules through the CREATE ROUTINE LOAD command.
tbl_name Clause
Specifies the name of the table to be imported. This is optional.
If not specified, dynamic table mode is used, where Kafka data needs to contain table name information. Currently, dynamic table names can only be obtained from Kafka's Value, and must conform to this format: in JSON format: table_name|{"col1": "val1", "col2": "val2"}, where tbl_name is the table name, with | as the separator between table name and table data. CSV format data is similar, for example: table_name|val1,val2,val3. Note that the table_name here must match the table name in Doris, otherwise import will fail. Note that dynamic tables do not support the column_mapping configuration introduced later.
merge_type Clause
You can specify the data merge type through the merge_type module. merge_type has three options:
-
APPEND: Append import mode
-
MERGE: Merge import mode. Only applicable to Unique Key model. Needs to be used with the [DELETE ON] module to mark the Delete Flag column
-
DELETE: All imported data is to be deleted
load_properties Clause
You can describe import data properties through the load_properties module. The specific syntax is as follows:
[COLUMNS TERMINATED BY <column_separator>,]
[COLUMNS (<column1_name>[, <column2_name>, <column_mapping>, ...]),]
[WHERE <where_expr>,]
[PARTITION(<partition1_name>, [<partition2_name>, <partition3_name>, ...]),]
[DELETE ON <delete_expr>,]
[ORDER BY <order_by_column1>[, <order_by_column2>, <order_by_column3>, ...]]
Specific module corresponding parameters are as follows:
| Sub-module | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| COLUMNS TERMINATED BY | <column_separator> | Used to specify the column separator. Default is \t. For example, to specify comma as the separator, use the following command: COLUMN TERMINATED BY ","For null value handling, note the following: - Null values need to be represented by - Empty strings ('') are directly left empty. The data |
| COLUMNS | <column_name> | Used to specify corresponding column names. For example, to specify import columns (k1, k2, k3), use the following command: COLUMNS(k1, k2, k3)The COLUMNS clause can be omitted in the following cases: - Columns in CSV correspond one-to-one with columns in the table - Key columns in JSON have the same names as columns in the table |
| <column_mapping> | During import, column mapping can be used for column filtering and transformation. For example, if the target column needs to be derived from a certain column of the data source during import, and target column k4 is calculated from column k3 using the formula k3+1, use the following command: COLUMNS(k1, k2, k3, k4 = k3 + 1)For details, refer to Data Transformation | |
| WHERE | <where_expr> | Specifying where_expr allows filtering of imported data sources based on conditions. For example, to only import data where age > 30, use the following command: WHERE age > 30 |
| PARTITION | <partition_name> | Specifies which partitions in the target table to import. If not specified, it will automatically import to the corresponding partition. For example, to import to partitions p1 and p2 of the target table, use the following command: PARTITION(p1, p2) |
| DELETE ON | <delete_expr> | In MERGE import mode, use delete_expr to mark which columns need to be deleted. For example, to delete columns where age > 30 during MERGE, use the following command: DELETE ON age > 30 |
| ORDER BY | <order_by_column> | Only effective for Unique Key model. Used to specify the Sequence Column in imported data to ensure data order. For example, when importing a Unique Key table, to specify the Sequence Column as create_time, use the following command: ORDER BY create_timeFor a description of the Sequence Column in the Unique Key model, refer to the documentation Data Update/Sequence Column |
job_properties Clause
When creating a Routine Load import job, you can specify the job_properties clause to specify properties of the import job. The syntax is as follows:
PROPERTIES ("<key1>" = "<value1>"[, "<key2>" = "<value2>" ...])
Specific parameter options for the job_properties clause are as follows:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| desired_concurrent_number | Default value: 256 Parameter description: The desired concurrency for a single import subtask (load task), modifying the number of desired import subtasks the Routine Load import job is split into. During import, the desired subtask concurrency may not equal the actual concurrency. The actual concurrency is comprehensively considered based on cluster node count, load, and data source conditions, using the following formula to calculate the actual number of import subtasks:
- topic_partition_num represents the number of partitions in the Kafka Topic - desired_concurrent_number represents the set parameter size - max_routine_load_task_concurrent_num is the parameter in FE that sets the maximum task concurrency for Routine Load |
| max_batch_interval | Maximum run time for each subtask, in seconds, must be greater than 0, default is 60(s). max_batch_interval/max_batch_rows/max_batch_size together form the subtask execution threshold. When any parameter reaches the threshold, the import subtask ends and a new import subtask is generated. |
| max_batch_rows | Maximum number of rows each subtask reads. Must be greater than or equal to 200000. Default is 20000000. max_batch_interval/max_batch_rows/max_batch_size together form the subtask execution threshold. When any parameter reaches the threshold, the import subtask ends and a new import subtask is generated. |
| max_batch_size | Maximum bytes each subtask reads. Unit is bytes, range is 100MB to 1GB. Default is 1G. max_batch_interval/max_batch_rows/max_batch_size together form the subtask execution threshold. When any parameter reaches the threshold, the import subtask ends and a new import subtask is generated. |
| max_error_number | Maximum allowed error rows within the sampling window. Must be greater than or equal to 0. Default is 0, meaning no error rows are allowed. The sampling window is max_batch_rows * 10. If the number of error rows in the sampling window is greater than max_error_number, the routine job will be paused, requiring manual intervention to check data quality issues through the ErrorLogUrls in the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD command. Rows filtered by where conditions are not counted as error rows. |
| strict_mode | Whether to enable strict mode, default is off. Strict mode means strict filtering of column type conversions during the import process. If enabled, non-null raw data whose column type conversion results in NULL will be filtered. Strict mode filtering strategy: - For derived columns (generated by function conversion), Strict Mode has no effect - When column types need conversion, incorrectly typed data will be filtered out, viewable in the - For imported columns containing range restrictions, if raw data can pass type conversion normally but cannot pass range restrictions, strict mode has no effect on it. For example: if the type is decimal(1,0), raw data is 10, it can pass type conversion but is not within the declared range. This data is not affected by strict mode. For details, refer to Strict Mode. |
| timezone | Specifies the timezone used for the import job. Default uses the Session's timezone parameter. This parameter affects all timezone-related function results involved in import. |
| format | Specifies the import data format, default is CSV, supports JSON format. |
| jsonpaths | When the import data format is JSON, you can specify fields to extract from JSON data through jsonpaths. For example, specify jsonpaths for import with the following command: "jsonpaths" = "[\"$.userid\",\"$.username\",\"$.age\",\"$.city\"]" |
| json_root | When the import data format is JSON, you can specify the root node of JSON data through json_root. Doris will extract elements from the root node for parsing. Default is empty. For example, specify the JSON root node for import with the following command: "json_root" = "$.RECORDS" |
| strip_outer_array | When the import data format is json, strip_outer_array being true means JSON data is presented as an array, with each element in the data treated as one row. Default value is false. Typically, JSON data in Kafka may be in array form, i.e., containing outer square brackets []. In this case, you can specify "strip_outer_array" = "true" to consume data in the Topic in array mode. For example, the following data will be parsed into two rows: [{"user_id":1,"name":"Emily","age":25},{"user_id":2,"name":"Benjamin","age":35}] |
| send_batch_parallelism | Used to set the parallelism for sending batch data. If the parallelism value exceeds max_send_batch_parallelism_per_job in the BE configuration, the BE serving as coordinator will use the value of max_send_batch_parallelism_per_job. |
| load_to_single_tablet | Supports importing data to only one tablet of the corresponding partition per task. Default value is false. This parameter is only allowed when importing data to olap tables with random bucketing. |
| partial_columns | Specifies whether to enable partial column update. Default value is false. This parameter is only allowed when the table model is Unique and uses Merge on Write. Multi-table streaming does not support this parameter. For details, refer to Partial Column Update |
| unique_key_update_mode | Specifies the update mode for Unique Key tables. Optional values:
|
| partial_update_new_key_behavior | Handling method for newly inserted rows when performing partial column updates on Unique Merge on Write tables. Two types: APPEND, ERROR.- APPEND: Allow insertion of new row data- ERROR: Import fails and reports an error when inserting new rows |
| max_filter_ratio | Maximum allowed filtering rate within the sampling window. Must be between greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1. Default value is 1.0, meaning any error rows can be tolerated. The sampling window is max_batch_rows * 10. If the error rows/total rows in the sampling window is greater than max_filter_ratio, the routine job will be paused, requiring manual intervention to check data quality issues. Rows filtered by where conditions are not counted as error rows. |
| enclose | Specifies the enclosing character. When CSV data fields contain row or column separators, a single-byte character can be specified as an enclosing character for protection. For example, if the column separator is "," and the enclosing character is "'", for data "a,'b,c'", "b,c" will be parsed as one field. |
| escape | Specifies the escape character. Used to escape characters in fields that are the same as the enclosing character. For example, if data is "a,'b,'c'", the enclosing character is "'", hoping "b,'c to be parsed as one field, you need to specify a single-byte escape character, such as "", and modify the data to "a,'b,'c'". |
04 data_source_properties Clause
When creating a Routine Load import job, you can specify the data_source_properties clause to specify properties of the Kafka data source. The syntax is as follows:
FROM KAFKA ("<key1>" = "<value1>"[, "<key2>" = "<value2>" ...])
Specific parameter options for the data_source_properties clause are as follows:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| kafka_broker_list | Specifies Kafka broker connection information. Format is <kafka_broker_ip>:<kafka port>. Multiple brokers are separated by commas. For example, in a Kafka Broker, the default port number is 9092. You can specify Broker List with the following command: "kafka_broker_list" = "<broker1_ip>:9092,<broker2_ip>:9092" |
| kafka_topic | Specifies the Kafka topic to subscribe to. One import job can only consume one Kafka Topic. |
| kafka_partitions | Specifies which Kafka Partitions to subscribe to. If not specified, all partitions are consumed by default. |
| kafka_offsets | Starting consumption point (offset) in the Kafka Partition to be consumed. If time is specified, consumption starts from the nearest offset greater than or equal to that time. Offset can specify a specific offset greater than or equal to 0, or use the following formats: - OFFSET_BEGINNING: Subscribe from the position where data exists. - OFFSET_END: Subscribe from the end. - Time format, such as: "2021-05-22 11:00:00" If not specified, it defaults to subscribing to all partitions under the topic starting from Multiple starting consumption points can be specified, separated by commas, such as: Note that time format and OFFSET format cannot be mixed. |
| property | Specifies custom kafka parameters. Functionally equivalent to the "--property" parameter in kafka shell. When the parameter Value is a file, you need to add the keyword "FILE:" before the Value. For creating files, refer to the CREATE FILE command documentation. For more supported custom parameters, refer to the client configuration items in librdkafka's official CONFIGURATION documentation. For example: "property.client.id" = "12345", "property.group.id" = "group_id_0", "property.ssl.ca.location" = "FILE:ca.pem". |
By configuring the kafka property parameters in data_source_properties, you can configure secure access options. Currently, Doris supports multiple Kafka security protocols, such as plaintext (default), SSL, PLAIN, Kerberos, etc.
Import Status
The import job status can be viewed through the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD command. The specific syntax is as follows:
SHOW [ALL] ROUTINE LOAD [FOR jobName];
For example, SHOW ROUTINE LOAD returns the following result set example:
mysql> SHOW ROUTINE LOAD FOR testdb.example_routine_load\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Id: 12025
Name: example_routine_load
CreateTime: 2024-01-15 08:12:42
PauseTime: NULL
EndTime: NULL
DbName: default_cluster:testdb
TableName: test_routineload_tbl
IsMultiTable: false
State: RUNNING
DataSourceType: KAFKA
CurrentTaskNum: 1
JobProperties: {"max_batch_rows":"200000","timezone":"America/New_York","send_batch_parallelism":"1","load_to_single_tablet":"false","column_separator":"','","line_delimiter":"\n","current_concurrent_number":"1","delete":"*","partial_columns":"false","merge_type":"APPEND","exec_mem_limit":"2147483648","strict_mode":"false","jsonpaths":"","max_batch_interval":"10","max_batch_size":"104857600","fuzzy_parse":"false","partitions":"*","columnToColumnExpr":"user_id,name,age","whereExpr":"*","desired_concurrent_number":"5","precedingFilter":"*","format":"csv","max_error_number":"0","max_filter_ratio":"1.0","json_root":"","strip_outer_array":"false","num_as_string":"false"}
DataSourceProperties: {"topic":"test-topic","currentKafkaPartitions":"0","brokerList":"192.168.88.62:9092"}
CustomProperties: {"kafka_default_offsets":"OFFSET_BEGINNING","group.id":"example_routine_load_73daf600-884e-46c0-a02b-4e49fdf3b4dc"}
Statistic: {"receivedBytes":28,"runningTxns":[],"errorRows":0,"committedTaskNum":3,"loadedRows":3,"loadRowsRate":0,"abortedTaskNum":0,"errorRowsAfterResumed":0,"totalRows":3,"unselectedRows":0,"receivedBytesRate":0,"taskExecuteTimeMs":30069}
Progress: {"0":"2"}
Lag: {"0":0}
ReasonOfStateChanged:
ErrorLogUrls:
OtherMsg:
User: root
Comment:
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Specific display result descriptions are as follows:
| Result Column | Column Description |
|---|---|
| Id | Job ID. Automatically generated by Doris. |
| Name | Job name. |
| CreateTime | Job creation time. |
| PauseTime | Most recent job pause time. |
| EndTime | Job end time. |
| DbName | Corresponding database name |
| TableName | Corresponding table name. In multi-table cases, since it's a dynamic table, the specific table name is not displayed; it shows multi-table. |
| IsMultiTbl | Whether it's multi-table. |
| State | Job running status. There are 5 states: - NEED_SCHEDULE: Job waiting to be scheduled. After CREATE ROUTINE LOAD or RESUME ROUTINE LOAD, the job first enters the NEED_SCHEDULE state; - RUNNING: Job is running; - PAUSED: Job is paused, can be resumed through RESUME ROUTINE LOAD; - STOPPED: Job has ended and cannot be restarted; - CANCELLED: Job has been cancelled. |
| DataSourceType | Data source type: KAFKA. |
| CurrentTaskNum | Current number of subtasks. |
| JobProperties | Job configuration details. |
| DataSourceProperties | Data source configuration details. |
| CustomProperties | Custom configuration. |
| Statistic | Job running status statistics. |
| Progress | Job running progress. For Kafka data sources, displays the currently consumed offset for each partition. For example, {"0":"2"} means the consumption progress for Kafka partition 0 is 2. |
| Lag | Job delay status. For Kafka data sources, displays the consumption lag for each partition. For example, {"0":10} means the consumption lag for Kafka partition 0 is 10. |
| ReasonOfStateChanged | Reason for job status change |
| ErrorLogUrls | Viewing address for filtered poor-quality data |
| OtherMsg | Other error messages |
Import Examples
Set Maximum Import Error Tolerance Rate
-
Sample import data
1,Benjamin,18
2,Emily,20
3,Alexander,dirty_data -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test01 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "User ID",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "Name",
age INT COMMENT "Age"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(`id`)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job01 ON routine_test01
COLUMNS TERMINATED BY ","
PROPERTIES
(
"max_filter_ratio"="0.5",
"max_error_number" = "100",
"strict_mode" = "true"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad01",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> select * from routine_test01;
+------+------------+------+
| id | name | age |
+------+------------+------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 |
| 2 | Emily | 20 |
+------+------------+------+
2 rows in set (0.01 sec)
Consume Data from Specified Consumption Point
-
Sample import data
1,Benjamin,18
2,Emily,20
3,Alexander,22
4,Sophia,24
5,William,26
6,Charlotte,28 -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test02 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "User ID",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "Name",
age INT COMMENT "Age"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(`id`)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job02 ON routine_test02
COLUMNS TERMINATED BY ","
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad02",
"kafka_partitions" = "0",
"kafka_offsets" = "3"
); -
Import result
mysql> select * from routine_test02;
+------+--------------+------+
| id | name | age |
+------+--------------+------+
| 4 | Sophia | 24 |
| 5 | William | 26 |
| 6 | Charlotte | 28 |
+------+--------------+------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
Specify Consumer Group's group.id and client.id
-
Sample import data
1,Benjamin,18
2,Emily,20
3,Alexander,22 -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test03 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "User ID",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "Name",
age INT COMMENT "Age"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(`id`)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job03 ON routine_test03
COLUMNS TERMINATED BY ","
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad01",
"property.group.id" = "kafka_job03",
"property.client.id" = "kafka_client_03",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> select * from routine_test03;
+------+------------+------+
| id | name | age |
+------+------------+------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 |
| 2 | Emily | 20 |
| 3 | Alexander | 22 |
+------+------------+------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
Set Import Filter Conditions
-
Sample import data
1,Benjamin,18
2,Emily,20
3,Alexander,22
4,Sophia,24
5,William,26
6,Charlotte,28 -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test04 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "User ID",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "Name",
age INT COMMENT "Age"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(`id`)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job04 ON routine_test04
COLUMNS TERMINATED BY ",",
WHERE id >= 3
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad04",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> select * from routine_test04;
+------+--------------+------+
| id | name | age |
+------+--------------+------+
| 4 | Sophia | 24 |
| 5 | William | 26 |
| 6 | Charlotte | 28 |
+------+--------------+------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
Import Specified Partition Data
-
Sample import data
1,Benjamin,18,2024-02-04 10:00:00
2,Emily,20,2024-02-05 11:00:00
3,Alexander,22,2024-02-06 12:00:00 -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test05 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "ID",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "Name",
age INT COMMENT "Age",
date DATETIME COMMENT "Date"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(`id`)
PARTITION BY RANGE(`id`)
(PARTITION partition_a VALUES [("0"), ("1")),
PARTITION partition_b VALUES [("1"), ("2")),
PARTITION partition_c VALUES [("2"), ("3")))
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job05 ON routine_test05
COLUMNS TERMINATED BY ",",
PARTITION(partition_b)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad05",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> select * from routine_test05;
+------+----------+------+---------------------+
| id | name | age | date |
+------+----------+------+---------------------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 | 2024-02-04 10:00:00 |
+------+----------+------+---------------------+
1 rows in set (0.01 sec)
Set Import Timezone
-
Sample import data
1,Benjamin,18,2024-02-04 10:00:00
2,Emily,20,2024-02-05 11:00:00
3,Alexander,22,2024-02-06 12:00:00 -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test06 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "id",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "name",
age INT COMMENT "age",
date DATETIME COMMENT "date"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(id)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(id) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job06 ON routine_test06
COLUMNS TERMINATED BY ","
PROPERTIES
(
"timezone" = "Asia/Shanghai"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad06",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> select * from routine_test06;
+------+-------------+------+---------------------+
| id | name | age | date |
+------+-------------+------+---------------------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 | 2024-02-04 10:00:00 |
| 2 | Emily | 20 | 2024-02-05 11:00:00 |
| 3 | Alexander | 22 | 2024-02-06 12:00:00 |
+------+-------------+------+---------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Set merge_type
Specify merge_type for Delete Operation
-
Sample import data
3,Alexander,22
5,William,26Data in table before import:
mysql> SELECT * FROM routine_test07;
+------+----------------+------+
| id | name | age |
+------+----------------+------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 |
| 2 | Emily | 20 |
| 3 | Alexander | 22 |
| 4 | Sophia | 24 |
| 5 | William | 26 |
| 6 | Charlotte | 28 |
+------+----------------+------+ -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test07 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "id",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "name",
age INT COMMENT "age"
)
UNIQUE KEY(id)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(id) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job07 ON routine_test07
WITH DELETE
COLUMNS TERMINATED BY ","
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad07",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> SELECT * FROM routine_test07;
+------+----------------+------+
| id | name | age |
+------+----------------+------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 |
| 2 | Emily | 20 |
| 4 | Sophia | 24 |
| 6 | Charlotte | 28 |
+------+----------------+------+
Specify merge_type for Merge Operation
-
Sample import data
1,xiaoxiaoli,28
2,xiaoxiaowang,30
3,xiaoxiaoliu,32
4,dadali,34
5,dadawang,36
6,dadaliu,38Data in table before import:
mysql> SELECT * FROM routine_test08;
+------+----------------+------+
| id | name | age |
+------+----------------+------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 |
| 2 | Emily | 20 |
| 3 | Alexander | 22 |
| 4 | Sophia | 24 |
| 5 | William | 26 |
| 6 | Charlotte | 28 |
+------+----------------+------+
6 rows in set (0.01 sec) -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test08 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "id",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "name",
age INT COMMENT "age"
)
UNIQUE KEY(id)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(id) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job08 ON routine_test08
WITH MERGE
COLUMNS TERMINATED BY ",",
DELETE ON id = 2
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad08",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> SELECT * FROM routine_test08;
+------+-------------+------+
| id | name | age |
+------+-------------+------+
| 1 | xiaoxiaoli | 28 |
| 3 | xiaoxiaoliu | 32 |
| 4 | dadali | 34 |
| 5 | dadawang | 36 |
| 6 | dadaliu | 38 |
+------+-------------+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Specify Sequence Column for Merge During Import
-
Sample import data
1,xiaoxiaoli,28
2,xiaoxiaowang,30
3,xiaoxiaoliu,32
4,dadali,34
5,dadawang,36
6,dadaliu,38Data in table before import:
mysql> SELECT * FROM routine_test09;
+------+----------------+------+
| id | name | age |
+------+----------------+------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 |
| 2 | Emily | 20 |
| 3 | Alexander | 22 |
| 4 | Sophia | 24 |
| 5 | William | 26 |
| 6 | Charlotte | 28 |
+------+----------------+------+
6 rows in set (0.01 sec) -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test08 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "id",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "name",
age INT COMMENT "age"
)
UNIQUE KEY(id)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(id) BUCKETS 1
PROPERTIES (
"function_column.sequence_col" = "age"
); -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job09 ON routine_test09
WITH MERGE
COLUMNS TERMINATED BY ",",
COLUMNS(id, name, age),
DELETE ON id = 2,
ORDER BY age
PROPERTIES
(
"desired_concurrent_number"="1",
"strict_mode" = "false"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad09",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> SELECT * FROM routine_test09;
+------+-------------+------+
| id | name | age |
+------+-------------+------+
| 1 | xiaoxiaoli | 28 |
| 3 | xiaoxiaoliu | 32 |
| 4 | dadali | 34 |
| 5 | dadawang | 36 |
| 6 | dadaliu | 38 |
+------+-------------+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Complete Column Mapping and Derived Column Calculation During Import
-
Sample import data
1,Benjamin,18
2,Emily,20
3,Alexander,22 -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test10 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "id",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "name",
age INT COMMENT "age",
num INT COMMENT "number"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(`id`)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job10 ON routine_test10
COLUMNS TERMINATED BY ",",
COLUMNS(id, name, age, num=age*10)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad10",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> SELECT * FROM routine_test10;
+------+----------------+------+------+
| id | name | age | num |
+------+----------------+------+------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 | 180 |
| 2 | Emily | 20 | 200 |
| 3 | Alexander | 22 | 220 |
+------+----------------+------+------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
Import Data with Enclosing Characters
-
Sample import data
1,"Benjamin",18
2,"Emily",20
3,"Alexander",22 -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test11 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "id",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "name",
age INT COMMENT "age",
num INT COMMENT "number"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(`id`)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job11 ON routine_test11
COLUMNS TERMINATED BY ","
PROPERTIES
(
"desired_concurrent_number"="1",
"enclose" = "\""
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad12",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> SELECT * FROM routine_test11;
+------+----------------+------+------+
| id | name | age | num |
+------+----------------+------+------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 | 180 |
| 2 | Emily | 20 | 200 |
| 3 | Alexander | 22 | 220 |
+------+----------------+------+------+
3 rows in set (0.02 sec)
JSON Format Import
Import JSON Format Data in Simple Mode
-
Sample import data
{ "id" : 1, "name" : "Benjamin", "age":18 }
{ "id" : 2, "name" : "Emily", "age":20 }
{ "id" : 3, "name" : "Alexander", "age":22 } -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test12 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "id",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "name",
age INT COMMENT "age"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(`id`)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job12 ON routine_test12
PROPERTIES
(
"format" = "json"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad12",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> select * from routine_test12;
+------+----------------+------+
| id | name | age |
+------+----------------+------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 |
| 2 | Emily | 20 |
| 3 | Alexander | 22 |
+------+----------------+------+
3 rows in set (0.02 sec)
Import Complex JSON Format Data in Matching Mode
-
Sample import data
{ "name" : "Benjamin", "id" : 1, "num":180 , "age":18 }
{ "name" : "Emily", "id" : 2, "num":200 , "age":20 }
{ "name" : "Alexander", "id" : 3, "num":220 , "age":22 } -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test13 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "id",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "name",
age INT COMMENT "age",
num INT COMMENT "num"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(`id`)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job13 ON routine_test13
COLUMNS(name, id, num, age)
PROPERTIES
(
"format" = "json",
"jsonpaths" = "[\"$.name\",\"$.id\",\"$.num\",\"$.age\"]"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad13",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> select * from routine_test13;
+------+----------------+------+------+
| id | name | age | num |
+------+----------------+------+------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 | 180 |
| 2 | Emily | 20 | 200 |
| 3 | Alexander | 22 | 220 |
+------+----------------+------+------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
Specify JSON Root Node to Import Data
-
Sample import data
{"id": 1231, "source" :{ "id" : 1, "name" : "Benjamin", "age":18 }}
{"id": 1232, "source" :{ "id" : 2, "name" : "Emily", "age":20 }}
{"id": 1233, "source" :{ "id" : 3, "name" : "Alexander", "age":22 }} -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test14 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "id",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "name",
age INT COMMENT "age"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(`id`)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job14 ON routine_test14
PROPERTIES
(
"format" = "json",
"json_root" = "$.source"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad14",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> select * from routine_test14;
+------+----------------+------+
| id | name | age |
+------+----------------+------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 |
| 2 | Emily | 20 |
| 3 | Alexander | 22 |
+------+----------------+------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
Complete Column Mapping and Derived Column Calculation During Import
-
Sample import data
{ "id" : 1, "name" : "Benjamin", "age":18 }
{ "id" : 2, "name" : "Emily", "age":20 }
{ "id" : 3, "name" : "Alexander", "age":22 } -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test15 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "id",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "name",
age INT COMMENT "age",
num INT COMMENT "num"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(`id`)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job15 ON routine_test15
COLUMNS(id, name, age, num=age*10)
PROPERTIES
(
"format" = "json"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad15",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> select * from routine_test15;
+------+----------------+------+------+
| id | name | age | num |
+------+----------------+------+------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 | 180 |
| 2 | Emily | 20 | 200 |
| 3 | Alexander | 22 | 220 |
+------+----------------+------+------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
Flexible Partial Column Update
This example demonstrates how to use flexible partial column update, where each row can update different columns. This is very useful in CDC scenarios where change records may contain different fields.
-
Sample import data (each JSON record updates different columns):
{"id": 1, "balance": 150.00, "last_active": "2024-01-15 10:30:00"}
{"id": 2, "city": "Shanghai", "age": 28}
{"id": 3, "name": "Alice", "balance": 500.00, "city": "Beijing"}
{"id": 1, "age": 30}
{"id": 4, "__DORIS_DELETE_SIGN__": 1} -
Create table (must enable Merge-on-Write and skip bitmap column):
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test_flexible (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "id",
name VARCHAR(30) COMMENT "Name",
age INT COMMENT "Age",
city VARCHAR(50) COMMENT "City",
balance DECIMAL(10,2) COMMENT "Balance",
last_active DATETIME COMMENT "Last Active Time"
)
UNIQUE KEY(`id`)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`) BUCKETS 1
PROPERTIES (
"replication_num" = "1",
"enable_unique_key_merge_on_write" = "true",
"enable_unique_key_skip_bitmap_column" = "true"
); -
Insert initial data:
INSERT INTO demo.routine_test_flexible VALUES
(1, 'John', 25, 'Shenzhen', 100.00, '2024-01-01 08:00:00'),
(2, 'Jane', 30, 'Guangzhou', 200.00, '2024-01-02 09:00:00'),
(3, 'Bob', 35, 'Hangzhou', 300.00, '2024-01-03 10:00:00'),
(4, 'Tom', 40, 'Nanjing', 400.00, '2024-01-04 11:00:00'); -
Import command:
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job_flexible ON routine_test_flexible
PROPERTIES
(
"format" = "json",
"unique_key_update_mode" = "UPDATE_FLEXIBLE_COLUMNS"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoadFlexible",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result:
mysql> SELECT * FROM demo.routine_test_flexible ORDER BY id;
+------+-------+------+-----------+---------+---------------------+
| id | name | age | city | balance | last_active |
+------+-------+------+-----------+---------+---------------------+
| 1 | John | 30 | Shenzhen | 150.00 | 2024-01-15 10:30:00 |
| 2 | Jane | 28 | Shanghai | 200.00 | 2024-01-02 09:00:00 |
| 3 | Alice | 35 | Beijing | 500.00 | 2024-01-03 10:00:00 |
+------+-------+------+-----------+---------+---------------------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)Note: The row with
id=4was deleted due to__DORIS_DELETE_SIGN__, and each row only updated the columns contained in its corresponding JSON record.
Import Complex Types
Import Array Data Type
-
Sample import data
{ "id" : 1, "name" : "Benjamin", "age":18, "array":[1,2,3,4,5]}
{ "id" : 2, "name" : "Emily", "age":20, "array":[6,7,8,9,10]}
{ "id" : 3, "name" : "Alexander", "age":22, "array":[11,12,13,14,15]} -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test16
(
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "id",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "name",
age INT COMMENT "age",
array ARRAY<int(11)> NULL COMMENT "test array column"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(`id`)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job16 ON routine_test16
PROPERTIES
(
"format" = "json"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad16",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> select * from routine_test16;
+------+----------------+------+----------------------+
| id | name | age | array |
+------+----------------+------+----------------------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 | [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] |
| 2 | Emily | 20 | [6, 7, 8, 9, 10] |
| 3 | Alexander | 22 | [11, 12, 13, 14, 15] |
+------+----------------+------+----------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Import Map Data Type
-
Sample import data
{ "id" : 1, "name" : "Benjamin", "age":18, "map":{"a": 100, "b": 200}}
{ "id" : 2, "name" : "Emily", "age":20, "map":{"c": 300, "d": 400}}
{ "id" : 3, "name" : "Alexander", "age":22, "map":{"e": 500, "f": 600}} -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test17 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "id",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "name",
age INT COMMENT "age",
map Map<STRING, INT> NULL COMMENT "test column"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(`id`)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job17 ON routine_test17
PROPERTIES
(
"format" = "json"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad17",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> select * from routine_test17;
+------+----------------+------+--------------------+
| id | name | age | map |
+------+----------------+------+--------------------+
| 1 | Benjamin | 18 | {"a":100, "b":200} |
| 2 | Emily | 20 | {"c":300, "d":400} |
| 3 | Alexander | 22 | {"e":500, "f":600} |
+------+----------------+------+--------------------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
Import Bitmap Data Type
-
Sample import data
{ "id" : 1, "name" : "Benjamin", "age":18, "bitmap_id":243}
{ "id" : 2, "name" : "Emily", "age":20, "bitmap_id":28574}
{ "id" : 3, "name" : "Alexander", "age":22, "bitmap_id":8573} -
Table structure
CREATE TABLE demo.routine_test18 (
id INT NOT NULL COMMENT "id",
name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT "name",
age INT COMMENT "age",
bitmap_id INT COMMENT "test",
device_id BITMAP BITMAP_UNION COMMENT "test column"
)
AGGREGATE KEY (`id`,`name`,`age`,`bitmap_id`)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`) BUCKETS 1; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job18 ON routine_test18
COLUMNS(id, name, age, bitmap_id, device_id=to_bitmap(bitmap_id))
PROPERTIES
(
"format" = "json"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad18",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> select id, BITMAP_UNION_COUNT(pv) over(order by id) uv from(
-> select id, BITMAP_UNION(device_id) as pv
-> from routine_test18
-> group by id
-> ) final;
+------+------+
| id | uv |
+------+------+
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
+------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Import HLL Data Type
-
Sample import data
2022-05-05,10001,Test01,Beijing,windows
2022-05-05,10002,Test01,Beijing,linux
2022-05-05,10003,Test01,Beijing,macos
2022-05-05,10004,Test01,Hebei,windows
2022-05-06,10001,Test01,Shanghai,windows
2022-05-06,10002,Test01,Shanghai,linux
2022-05-06,10003,Test01,Jiangsu,macos
2022-05-06,10004,Test01,Shaanxi,windows -
Table structure
create table demo.routine_test19 (
dt DATE,
id INT,
name VARCHAR(10),
province VARCHAR(10),
os VARCHAR(10),
pv hll hll_union
)
Aggregate KEY (dt,id,name,province,os)
distributed by hash(id) buckets 10; -
Import command
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job19 ON routine_test19
COLUMNS TERMINATED BY ",",
COLUMNS(dt, id, name, province, os, pv=hll_hash(id))
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "10.16.10.6:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad19",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
); -
Import result
mysql> select * from routine_test19;
+------------+-------+----------+----------+---------+------+
| dt | id | name | province | os | pv |
+------------+-------+----------+----------+---------+------+
| 2022-05-05 | 10001 | Test01 | Beijing | windows | NULL |
| 2022-05-06 | 10001 | Test01 | Shanghai | windows | NULL |
| 2022-05-05 | 10002 | Test01 | Beijing | linux | NULL |
| 2022-05-06 | 10002 | Test01 | Shanghai | linux | NULL |
| 2022-05-05 | 10004 | Test01 | Hebei | windows | NULL |
| 2022-05-06 | 10004 | Test01 | Shaanxi | windows | NULL |
| 2022-05-05 | 10003 | Test01 | Beijing | macos | NULL |
| 2022-05-06 | 10003 | Test01 | Jiangsu | macos | NULL |
+------------+-------+----------+----------+---------+------+
8 rows in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> SELECT HLL_UNION_AGG(pv) FROM routine_test19;
+-------------------+
| hll_union_agg(pv) |
+-------------------+
| 4 |
+-------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
Kafka Security Authentication
Import Data from SSL-Authenticated Kafka
Sample import command:
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job20 ON routine_test20
PROPERTIES
(
"format" = "json"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "192.168.100.129:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad21",
"property.security.protocol" = "ssl",
"property.ssl.ca.location" = "FILE:ca.pem",
"property.ssl.certificate.location" = "FILE:client.pem",
"property.ssl.key.location" = "FILE:client.key",
"property.ssl.key.password" = "ssl_passwd"
);
Parameter description:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| property.security.protocol | Security protocol used, such as SSL in the above example |
| property.ssl.ca.location | Location of CA (Certificate Authority) certificate |
| property.ssl.certificate.location | (Required only if Kafka server has client authentication enabled) Location of Client's public key |
| property.ssl.key.location | (Required only if Kafka server has client authentication enabled) Location of Client's private key |
| property.ssl.key.password | (Required only if Kafka server has client authentication enabled) Password for Client's private key |
Import Data from Kerberos-Authenticated Kafka
Sample import command:
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job21 ON routine_test21
PROPERTIES
(
"format" = "json"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "192.168.100.129:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad21",
"property.security.protocol" = "SASL_PLAINTEXT",
"property.sasl.kerberos.service.name" = "kafka",
"property.sasl.kerberos.keytab"="/opt/third/kafka/kerberos/kafka_client.keytab",
"property.sasl.kerberos.principal" = "clients/stream.dt.local@EXAMPLE.COM"
);
Parameter description:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| property.security.protocol | Security protocol used, such as SASL_PLAINTEXT in the above example |
| property.sasl.kerberos.service.name | Specifies broker service name, default is Kafka |
| property.sasl.kerberos.keytab | Location of keytab file |
| property.sasl.kerberos.principal | Specifies kerberos principal |
It's recommended to set
rdnbs=trueinkrb5.conf. Otherwise, you may encounter an error:Server kafka/15.5.4.68@EXAMPLE.COM not found in Kerberos database
Import from PLAIN-Authenticated Kafka Cluster
Sample import command:
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD demo.kafka_job22 ON routine_test22
PROPERTIES
(
"format" = "json"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "192.168.100.129:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "routineLoad22",
"property.security.protocol"="SASL_PLAINTEXT",
"property.sasl.mechanism"="PLAIN",
"property.sasl.username"="admin",
"property.sasl.password"="admin"
);
Parameter description:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| property.security.protocol | Security protocol used, such as SASL_PLAINTEXT in the above example |
| property.sasl.mechanism | Specifies SASL authentication mechanism as PLAIN |
| property.sasl.username | SASL username |
| property.sasl.password | SASL password |
Multi-Table Import from Single Stream
Create a Kafka routine dynamic multi-table import task named test1 for example_db. Specify column separator and group.id and client.id, automatically consume all partitions by default, and start subscribing from the position where data exists (OFFSET_BEGINNING).
Here we assume we need to import data from Kafka into both tbl1 and tbl2 tables in example_db. We create a routine import task named test1 that imports data from the Kafka Topic named my_topic into both tbl1 and tbl2 simultaneously. This allows one routine import task to import Kafka data into two tables.
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD example_db.test1
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "broker1:9092,broker2:9092,broker3:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "my_topic",
"property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
);
At this point, the data in Kafka needs to contain table name information. Currently, dynamic table names can only be obtained from Kafka's Value, and must conform to this format: in JSON format: table_name|{"col1": "val1", "col2": "val2"}, where tbl_name is the table name, with | as the separator between table name and table data. CSV format data is similar, for example: table_name|val1,val2,val3. Note that the table_name here must match the table name in Doris, otherwise import will fail. Note that dynamic tables do not support the column_mapping configuration introduced later.
Strict Mode Import
Create a Kafka routine import task named test1 for example_tbl in example_db. The import task is in strict mode.
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD example_db.test1 ON example_tbl
COLUMNS(k1, k2, k3, v1, v2, v3 = k1 * 100),
PRECEDING FILTER k1 = 1,
WHERE k1 < 100 and k2 like "%doris%"
PROPERTIES
(
"strict_mode" = "true"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "broker1:9092,broker2:9092,broker3:9092",
"kafka_topic" = "my_topic"
);
Connect to Encrypted and Authenticated Kafka Service
Here we use accessing StreamNative messaging service as an example:
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD example_db.test1 ON example_tbl
COLUMNS(user_id, name, age)
FROM KAFKA (
"kafka_broker_list" = "pc-xxxx.aws-mec1-test-xwiqv.aws.snio.cloud:9093",
"kafka_topic" = "my_topic",
"property.security.protocol" = "SASL_SSL",
"property.sasl.mechanism" = "PLAIN",
"property.sasl.username" = "user",
"property.sasl.password" = "token:eyJhbxxx",
"property.group.id" = "my_group_id_1",
"property.client.id" = "my_client_id_1",
"property.enable.ssl.certificate.verification" = "false"
);
Note: If the trusted CA certificate path is not configured on the BE side, you need to set "property.enable.ssl.certificate.verification" = "false" to not verify whether the server certificate is trusted.
Otherwise, you need to configure the trusted CA certificate path: "property.ssl.ca.location" = "/path/to/ca-cert.pem".
More Help
Refer to the SQL manual Routine Load. You can also enter HELP ROUTINE LOAD in the client command line to get more help information.
