Stream Load
Stream Load supports importing local files or data streams into Doris through the HTTP protocol.
Stream Load is a synchronous import method that returns the import result after the import is executed, allowing you to determine the success of the import through the request response. Generally, users can use Stream Load to import files under 10GB. If the file is too large, it is recommended to split the file and then use Stream Load for importing. Stream Load can ensure the atomicity of a batch of import tasks, meaning that either all of them succeed or all of them fail.
In comparison to single-threaded load using curl, Doris Streamloader is a client tool designed for loading data into Apache Doris. It reduces the ingestion latency of large datasets by its concurrent loading capabilities. It comes with the following features:
- Parallel loading: multi-threaded load for the Stream Load method. You can set the parallelism level using the
workersparameter. - Multi-file load: simultaneously loading of multiple files and directories with one shot. It supports recursive file fetching and allows you to specify file names with wildcard characters.
- Path traversal support: supports path traversal when the source files are in directories
- Resilience and continuity: in case of partial load failures, it can resume data loading from the point of failure.
- Automatic retry mechanism: in case of loading failures, it can automatically retry a default number of times. If the loading remains unsuccessful, it will print the command for manual retry.
See Doris Streamloader for detailed instructions and best practices.
User guide
Stream Load supports importing CSV, JSON, Parquet, and ORC format data from local or remote sources via HTTP.
- Null values: Use
\Nto represent null. For example,a,\N,bindicates the middle column is null. - Empty string: An empty string is represented when there are no characters between two delimiters. For example, in
a,,b, there are no characters between the two commas, indicating that the middle column value is an empty string.
Basic principles
When using Stream Load, it is necessary to initiate an import job through the HTTP protocol to the FE (Frontend) node. The FE will redirect the request to a BE (Backend) node in a round-robin manner to achieve load balancing. It is also possible to send HTTP requests directly to a specific BE node. In Stream Load, Doris selects one node to serve as the Coordinator node. The Coordinator node is responsible for receiving data and distributing it to other nodes.
The following figure shows the main flow of Stream Load, omitting some import details.
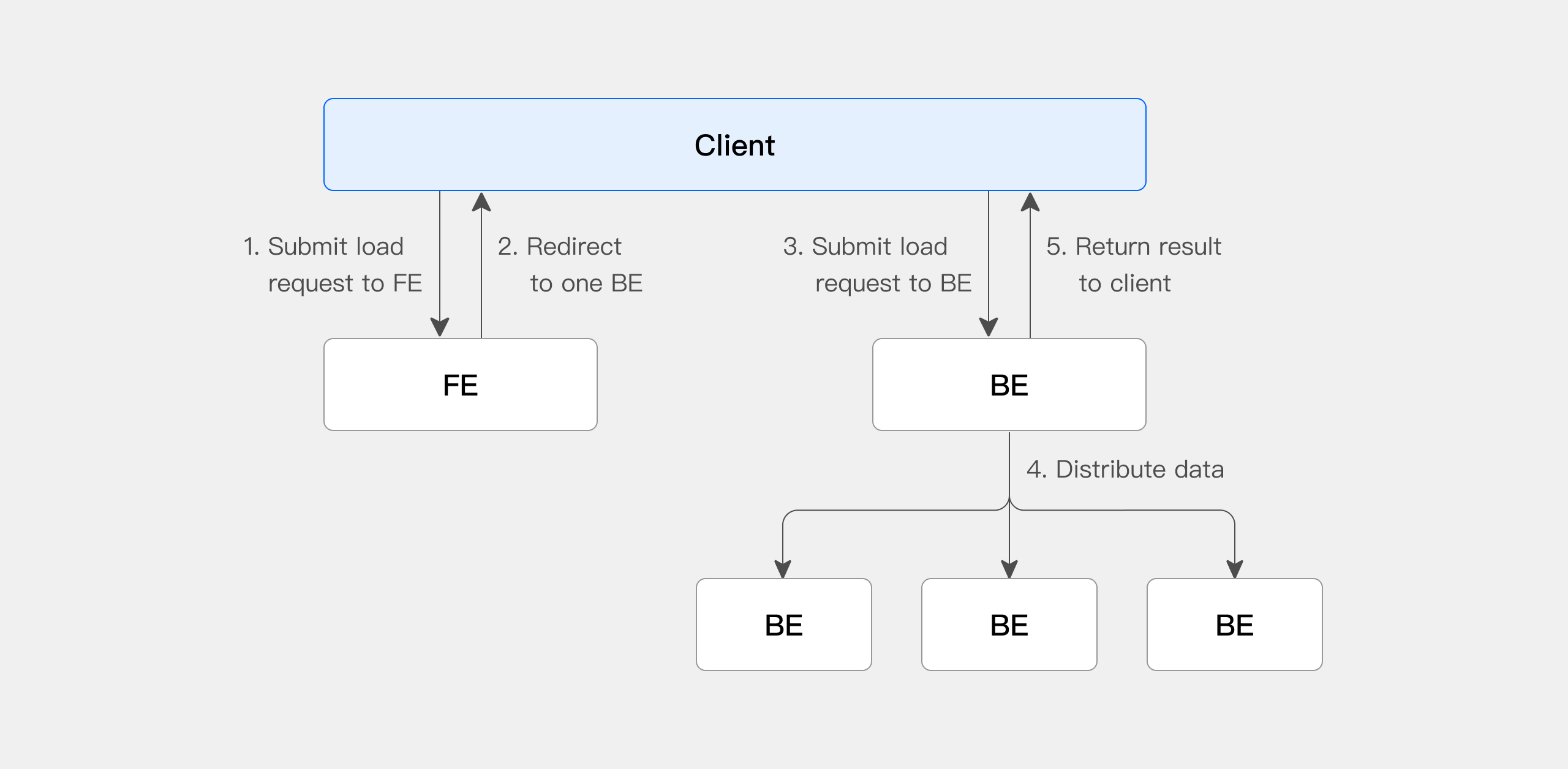
- The client submits a Stream Load imports job request to the FE (Frontend).
- The FE selects a BE (Backend) as the Coordinator node in a round-robin manner, which is responsible for scheduling the import job, and then returns an HTTP redirect to the client.
- The client connects to the Coordinator BE node and submits the import request.
- The Coordinator BE distributes the data to the appropriate BE nodes and returns the import result to the client once the import is complete.
- Alternatively, the client can directly specify a BE node as the Coordinator and distribute the import job directly.
Quick start
Stream Load import data through the HTTP protocol. The following example uses the curl tool to demonstrate submitting an import job through Stream Load.
Prerequisite check
Stream Load requires INSERT privileges on the target table. If there are no INSERT privileges, it can be granted to the user through the GRANT command.
Create load job
Loading CSV
-
Creating loading data
Create a CSV file named
streamload_example.csv. The specific content is as follows
1,Emily,25
2,Benjamin,35
3,Olivia,28
4,Alexander,60
5,Ava,17
6,William,69
7,Sophia,32
8,James,64
9,Emma,37
10,Liam,64
-
Creating a table for loading
Create the table that will be imported into, using the specific syntax as follows:
CREATE TABLE testdb.test_streamload(
user_id BIGINT NOT NULL COMMENT "User ID",
name VARCHAR(20) COMMENT "User name",
age INT COMMENT "User age"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(user_id)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(user_id) BUCKETS 10;
-
Enable the load job
The Stream Load job can be submitted using the
curlcommand.
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "column_separator:," \
-H "columns:user_id,name,age" \
-T streamload_example.csv \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Stream Load is a synchronous method, where the result is directly returned to the user.
{
"TxnId": 3,
"Label": "123",
"Comment": "",
"TwoPhaseCommit": "false",
"Status": "Success",
"Message": "OK",
"NumberTotalRows": 10,
"NumberLoadedRows": 10,
"NumberFilteredRows": 0,
"NumberUnselectedRows": 0,
"LoadBytes": 118,
"LoadTimeMs": 173,
"BeginTxnTimeMs": 1,
"StreamLoadPutTimeMs": 70,
"ReadDataTimeMs": 2,
"WriteDataTimeMs": 48,
"CommitAndPublishTimeMs": 52
}
- View data
mysql> select count(*) from testdb.test_streamload;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 10 |
+----------+
Loading JSON
- Creating loading data
Create a JSON file named streamload_example.json . The specific content is as follows
[
{"userid":1,"username":"Emily","userage":25},
{"userid":2,"username":"Benjamin","userage":35},
{"userid":3,"username":"Olivia","userage":28},
{"userid":4,"username":"Alexander","userage":60},
{"userid":5,"username":"Ava","userage":17},
{"userid":6,"username":"William","userage":69},
{"userid":7,"username":"Sophia","userage":32},
{"userid":8,"username":"James","userage":64},
{"userid":9,"username":"Emma","userage":37},
{"userid":10,"username":"Liam","userage":64}
]
-
Creating a table for loading
Create the table that will be imported into, using the specific syntax as follows:
CREATE TABLE testdb.test_streamload(
user_id BIGINT NOT NULL COMMENT "User ID",
name VARCHAR(20) COMMENT "User name",
age INT COMMENT "User age"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(user_id)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(user_id) BUCKETS 10;
-
Enabling the load job
The Stream Load job can be submitted using the
curlcommand.
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "label:124" \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "format:json" -H "strip_outer_array:true" \
-H "jsonpaths:[\"$.userid\", \"$.username\", \"$.userage\"]" \
-H "columns:user_id,name,age" \
-T streamload_example.json \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
If the JSON file is not a JSON array but each line is a JSON object, add the headers -H "strip_outer_array:false" and -H "read_json_by_line:true".
If you need to load the JSON object at the root node of a JSON file, the jsonpaths should be specified as ., e.g., `-H "jsonpaths:[\"."]`"
Stream Load is a synchronous method, where the result is directly returned to the user.
{
"TxnId": 7,
"Label": "125",
"Comment": "",
"TwoPhaseCommit": "false",
"Status": "Success",
"Message": "OK",
"NumberTotalRows": 10,
"NumberLoadedRows": 10,
"NumberFilteredRows": 0,
"NumberUnselectedRows": 0,
"LoadBytes": 471,
"LoadTimeMs": 52,
"BeginTxnTimeMs": 0,
"StreamLoadPutTimeMs": 11,
"ReadDataTimeMs": 0,
"WriteDataTimeMs": 23,
"CommitAndPublishTimeMs": 16
}
View load job
By default, Stream Load synchronously returns results to the client, so the system does not record Stream Load historical jobs. If recording is required, add the configuration enable_stream_load_record=true in be.conf. Refer to the BE configuration options for specific details.
After configuring, you can use the show stream load command to view completed Stream Load jobs.
mysql> show stream load from testdb;
+-------+--------+-----------------+---------------+---------+---------+------+-----------+------------+--------------+----------------+-----------+-------------------------+-------------------------+------+---------+
| Label | Db | Table | ClientIp | Status | Message | Url | TotalRows | LoadedRows | FilteredRows | UnselectedRows | LoadBytes | StartTime | FinishTime | User | Comment |
+-------+--------+-----------------+---------------+---------+---------+------+-----------+------------+--------------+----------------+-----------+-------------------------+-------------------------+------+---------+
| 12356 | testdb | test_streamload | 192.168.88.31 | Success | OK | N/A | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 118 | 2023-11-29 08:53:00.594 | 2023-11-29 08:53:00.650 | root | |
+-------+--------+-----------------+---------------+---------+---------+------+-----------+------------+--------------+----------------+-----------+-------------------------+-------------------------+------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Choosing Compute Group
Users can specify a particular Compute Group for Stream Load to run on.
Under the storage-computation separation mode, Compute Groups can be specified in the following ways:
- Specify via an HTTP Header parameter.
-H "cloud_cluster:cluster1"
Starting from Doris 4.0.0, you can use compute_group as an alternative
-H "compute_group:cluster1"
- Specify Compute Group in the user properties bound to Stream Load. If both user properties and the HTTP header specify a Compute Group, the Compute Group specified in the Header takes precedence.
set property for user1 'default_compute_group'='cluster1';
- If neither user properties nor the HTTP Header specify a Compute Group, a Compute Group that the user bound to Stream Load has permission to access will be selected. If the user does not have permission to access any Compute Group, the Load will fail.
Under the integrated storage-computation mode, specifying a Compute Group is only supported through the user properties bound to Stream Load.
If not specified in the user properties, the Compute Group named default will be selected.
set property for user1 'resource_tags.location'='group_1';
Cancel load job
Users cannot manually cancel a Stream Load operation. A Stream Load job will be automatically canceled by the system if it encounters a timeout (set to 0) or an import error.
Reference manual
Command
The syntax for Stream Load is as follows:
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" [-H ""...] \
-T <file_path> \
-XPUT http://fe_host:http_port/api/{db}/{table}/_stream_load
Stream Load operation supports both HTTP chunked and non-chunked import methods. For non-chunked imports, it is necessary to have a Content-Length header to indicate the length of the uploaded content, which ensures data integrity.
Load configuration parameters
FE configuration
-
stream_load_default_timeout_second-
Default Value: 259200 (s)
-
Dynamic Configuration: Yes
-
FE Master-only Configuration: Yes
-
Parameter Description: The default timeout for Stream Load. The load job will be canceled by the system if it is not completed within the set timeout (in seconds). If the source file cannot be imported within the specified time, the user can set an individual timeout in the Stream Load request. Alternatively, adjust the stream_load_default_timeout_second parameter on the FE to set the global default timeout.
BE configuration
-
streaming_load_max_mb- Default value: 10240 (MB)
- Dynamic configuration: Yes
- Parameter description: The maximum import size for Stream Load. If the user's original file exceeds this value, the
streaming_load_max_mbparameter on the BE needs to be adjusted.
-
Header parameters
Load parameters can be passed through the HTTP Header section. See below for specific parameter descriptions.
| Parameters | Parameters description |
|---|---|
| label | Used to specify a label for this Doris import. Data with the same label cannot be imported multiple times. If no label is specified, Doris will automatically generate one. Users can avoid duplicate imports of the same data by specifying a label. Doris retains import job labels for three days by default, but this duration can be adjusted using label_keep_max_second. For example, to specify the label for this import as 123, use the command -H "label:123". The use of labels prevents users from importing the same data repeatedly. It is strongly recommended that users use the same label for the same batch of data. This ensures that duplicate requests for the same batch of data are only accepted once, guaranteeing At-Most-Once semantics. When the status of an import job corresponding to a label is CANCELLED, that label can be used again. |
| column_separator | Used to specify the column separator in the import file, which defaults to \t. If the separator is an invisible character, it needs to be prefixed with \x and represented in hexadecimal format. Multiple characters can be combined as a column separator. For example, to specify the separator as \x01 for a Hive file, use the command -H "column_separator:\x01". |
| line_delimiter | Used to specify the line delimiter in the import file, which defaults to \n. Multiple characters can be combined as a line delimiter. For example, to specify the line delimiter as \n, use the command -H "line_delimiter:\n". |
| columns | Used to specify the correspondence between columns in the import file and columns in the table. If the columns in the source file exactly match the content of the table, this field does not need to be specified. If the schema of the source file does not match the table, this field is required for data transformation. There are two formats: direct column correspondence to fields in the import file, and derived columns represented by expressions. Refer to Data Transformation for detailed examples. |
| where | Used to filter out unnecessary data. If users need to exclude certain data, they can achieve this by setting this option. For example, to import only data where the k1 column is equal to 20180601, specify -H "where: k1 = 20180601" during the import. |
| max_filter_ratio | Used to specify the maximum tolerable ratio of filterable (irregular or otherwise problematic) data, which defaults to zero tolerance. The value range is 0 to 1. If the error rate of the imported data exceeds this value, the import will fail. Irregular data does not include rows filtered out by the where condition. For example, to maximize the import of all correct data (100% tolerance), specify the command -H "max_filter_ratio:1". |
| partitions | Used to specify the partitions involved in this import. If users can determine the corresponding partitions for the data, it is recommended to specify this option. Data that does not meet these partition criteria will be filtered out. For example, to specify importing into partitions p1 and p2, use the command -H "partitions: p1, p2". |
| timeout | Used to specify the timeout for the import in seconds. The default is 600 seconds, and the configurable range is from 1 second to 259200 seconds. For example, to specify an import timeout of 1200 seconds, use the command -H "timeout:1200". |
| strict_mode | Used to specify whether to enable strict mode for this import, which is disabled by default. For example, to enable strict mode, use the command -H "strict_mode:true". |
| timezone | Used to specify the timezone to be used for this import, which defaults to GMT+8. This parameter affects the results of all timezone-related functions involved in the import. For example, to specify the import timezone as Africa/Abidjan, use the command -H "timezone:Africa/Abidjan". |
| exec_mem_limit | The memory limit for the import, which defaults to 2GB. The unit is bytes. |
| format | Used to specify the format of the imported data, which defaults to CSV. Currently supported formats include: CSV, JSON, arrow, csv_with_names (supports filtering the first row of the csv file), csv_with_names_and_types (supports filtering the first two rows of the csv file), Parquet, and ORC. For example, to specify the imported data format as JSON, use the command -H "format:json". |
| jsonpaths | There are two ways to import JSON data format: Simple Mode and Matching Mode. If no jsonpaths are specified, it is the simple mode that requires the JSON data to be of the object type.Matching mode used when the JSON data is relatively complex and requires matching the corresponding values through the jsonpaths parameter.In simple mode, the keys in JSON are required to correspond one-to-one with the column names in the table. For example, in the JSON data {"k1":1, "k2":2, "k3":"hello"}, k1, k2, and k3 correspond to the columns in the table respectively. |
| strip_outer_array | When strip_outer_array is set to true, it indicates that the JSON data starts with an array object and flattens the objects within the array. The default value is false. When the outermost layer of the JSON data is represented by [], which denotes an array, strip_outer_array should be set to true. For example, with the following data, setting strip_outer_array to true will result in two rows of data being generated when imported into Doris: [{"k1": 1, "v1": 2}, {"k1": 3, "v1": 4}]. |
| json_root | json_root is a valid jsonpath string that specifies the root node of a JSON document, with a default value of "". |
| merge_type | The merge type of data. Three types are supported: - APPEND (default): Indicates that all data in this batch will be appended to existing data - DELETE: Indicates deletion of all rows with Keys matching this batch of data - MERGE: Must be used in conjunction with DELETE conditions. Data meeting DELETE conditions will be processed according to DELETE semantics, while the rest will be processed according to APPEND semantics For example, to specify merge mode as MERGE: -H "merge_type: MERGE" -H "delete: flag=1" |
| delete | It is only meaningful under MERGE, representing the deletion conditions for data. |
| function_column.sequence_col | It is suitable only for the UNIQUE KEYS model. Within the same Key column, it ensures that the Value column is replaced according to the specified source_sequence column. The source_sequence can either be a column from the data source or an existing column in the table structure. |
| fuzzy_parse | It is a boolean type. If set to true, the JSON will be parsed with the first row as the schema. Enabling this option can improve the efficiency of JSON imports, but it requires that the order of the keys in all JSON objects be consistent with the first line. The default is false and it is only used for JSON format. |
| num_as_string | It is a boolean type. When set to true, indicates that numeric types will be converted to strings during JSON parsing to ensure no loss of precision during the import process. |
| read_json_by_line | It is a boolean type. When set to true, indicates support for reading one JSON object per line, defaulting to false. |
| send_batch_parallelism | Sets the parallelism for the parallelism for sending batch-processed data. If the parallelism value exceeds the max_send_batch_parallelism_per_job configured in BE, the coordinating BE will use the max_send_batch_parallelism_per_job value. |
| hidden_columns | Used to specify hidden columns in the imported data, which takes effect when the Header does not include Columns. Multiple hidden columns are separated by commas. The system will use the user-specified data for import. In the following example, the last column of data in the imported data is __DORIS_SEQUENCE_COL__. hidden_columns: __DORIS_DELETE_SIGN__,__DORIS_SEQUENCE_COL__. |
| load_to_single_tablet | It is a boolean type. When set to true, indicates support for importing data only to a single Tablet corresponding to the partition, defaulting to false. This parameter is only allowed when importing to an OLAP table with random bucketing. |
| compress_type | Currently, only compression of CSV files is supported. Compression formats include gz, lzo, bz2, lz4, lzop, and deflate. |
| trim_double_quotes | It is a boolean type. When set to true, indicates trimming of the outermost double quotes for each field in the CSV file, defaulting to false. |
| skip_lines | It is an integer type. Used to specify the number of lines to skip at the beginning of the CSV file, defaulting to 0. When the format is set to csv_with_names or csv_with_names_and_types, this parameter will become invalid. |
| comment | It is a String type, with an empty string as the default value. Used to add additional information to the task. |
| enclose | Specify the enclosure character. When a CSV data field contains a row delimiter or column delimiter, to prevent unexpected truncation, you can specify a single-byte character as the enclosure for protection. For example, if the column delimiter is "," and the enclosure is "'", the data "a,'b,c'" will have "b,c" parsed as a single field. Note: When the enclosure is set to a double quote ("), make sure to set trim_double_quotes to true. |
| escape | Specify the escape character. It is used to escape characters that are the same as the enclosure character within a field. For example, if the data is "a,'b,'c'", and the enclosure is "'", and you want "b,'c" to be parsed as a single field, you need to specify a single-byte escape character, such as "", and modify the data to "a,'b','c'". |
| memtable_on_sink_node | Whether to enable MemTable on DataSink node when loading data, default is false. |
| unique_key_update_mode | The update modes on Unique tables, currently are only effective for Merge-On-Write Unique tables. Supporting three types: UPSERT, UPDATE_FIXED_COLUMNS, and UPDATE_FLEXIBLE_COLUMNS. UPSERT: Indicates that data is loaded with upsert semantics; UPDATE_FIXED_COLUMNS: Indicates that data is loaded through partial updates; UPDATE_FLEXIBLE_COLUMNS: Indicates that data is loaded through flexible partial updates. |
| partial_update_new_key_behavior | When performing partial column updates or flexible column updates on Unique tables, this parameter controls how new rows are handled. There are two types: APPEND and ERROR.- APPEND: Allows inserting new row data- ERROR: Fails and reports an error when inserting new rows |
Load return value
Stream Load is a synchronous import method, and the load result is directly provided to the user through the creation of an load return value, as shown below:
{
"TxnId": 1003,
"Label": "b6f3bc78-0d2c-45d9-9e4c-faa0a0149bee",
"Status": "Success",
"ExistingJobStatus": "FINISHED", // optional
"Message": "OK",
"NumberTotalRows": 1000000,
"NumberLoadedRows": 1000000,
"NumberFilteredRows": 1,
"NumberUnselectedRows": 0,
"LoadBytes": 40888898,
"LoadTimeMs": 2144,
"BeginTxnTimeMs": 1,
"StreamLoadPutTimeMs": 2,
"ReadDataTimeMs": 325,
"WriteDataTimeMs": 1933,
"CommitAndPublishTimeMs": 106,
"ErrorURL": "http://192.168.1.1:8042/api/_load_error_log?file=__shard_0/error_log_insert_stmt_db18266d4d9b4ee5-abb00ddd64bdf005_db18266d4d9b4ee5_abb00ddd64bdf005"
}
The return result parameters are explained in the following table:
| Parameters | Parameters description |
|---|---|
| TxnId | Import transaction ID |
| Label | Label of load job,specified via -H "label:<label_id>". |
| Status | Final load Status. Success: The load job was successful.Publish Timeout: The load job has been completed, but there may be a delay in data visibility. Label Already Exists: The label is duplicated, requiring a new label. Fail: The load job failed. |
| ExistingJobStatus | The status of the load job corresponding to the already existing label. This field is only displayed when the Status is Label Already Exists. Users can use this status to know the status of the import job corresponding to the existing label. RUNNING means the job is still executing, and FINISHED means the job was successful. |
| Message | Error information related to the load job. |
| NumberTotalRows | The total number of rows processed during the load job. |
| NumberLoadedRows | The number of rows that were successfully loaded. |
| NumberFilteredRows | The number of rows that did not meet the data quality standards. |
| NumberUnselectedRows | The number of rows that were filtered out based on the WHERE condition. |
| LoadBytes | The amount of data in bytes. |
| LoadTimeMs | The time taken for the load job to complete, measured in milliseconds. |
| BeginTxnTimeMs | The time taken to request the initiation of a transaction from the Frontend node (FE), measured in milliseconds. |
| StreamLoadPutTimeMs | The time taken to request the execution plan for the load job data from the FE, measured in milliseconds. |
| ReadDataTimeMs | The time spent reading the data during the load job, measured in milliseconds. |
| WriteDataTimeMs | The time taken to perform the data writing operations during the load job, measured in milliseconds. |
| CommitAndPublishTimeMs | The time taken to request the commit and publish the transaction from the FE, measured in milliseconds. |
| ErrorURL | If there are data quality issues, users can access this URL to view the specific rows with errors. |
Users can access the ErrorURL to review data that failed to import due to issues with data quality. By executing the command curl "<ErrorURL>", users can directly retrieve information about the erroneous data.
Load example
Setting load timeout and maximum size
The timeout for a load job is measured in seconds. If the load job is not completed within the specified timeout period, it will be cancelled by the system and marked as CANCELLED. You can adjust the timeout for a Stream Load job by specifying the timeout parameter or adding the stream_load_default_timeout_second parameter in the fe.conf file.
Before initiating the load, you need to calculate the timeout based on the file size. For example, for a 100GB file with an estimated load performance of 50MB/s:
Load time ≈ 100GB / 50MB/s ≈ 2048s
You can use the following command to specify a timeout of 3000 seconds for creating a Stream Load job:
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "timeout:3000"
-H "column_separator:," \
-H "columns:user_id,name,age" \
-T streamload_example.csv \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Setting maximum error tolerance rate
Load job can tolerate a certain amount of data with formatting errors. The tolerance rate is configured using the max_filter_ratio parameter. By default, it is set to 0, meaning that if there is even a single erroneous data row, the entire load job will fail. If users wish to ignore some problematic data rows, they can set this parameter to a value between 0 and 1. Doris will automatically skip rows with incorrect data formats. For more information on calculating the tolerance rate, please refer to the Data Transformation documentation.
You can use the following command to specify a max_filter_ratio tolerance of 0.4 for creating a Stream Load job:
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "max_filter_ratio:0.4" \
-H "column_separator:," \
-H "columns:user_id,name,age" \
-T streamload_example.csv \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Setting load filtering conditions
During the load job, you can use the WHERE parameter to apply conditional filtering to the imported data. The filtered data will not be included in the calculation of the filter ratio and will not affect the setting of max_filter_ratio. After the load job is complete, you can view the number of filtered rows by checking num_rows_unselected.
You can use the following command to specify WHERE filtering conditions for creating a Stream Load job:
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "where:age>=35" \
-H "column_separator:," \
-H "columns:user_id,name,age" \
-T streamload_example.csv \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Loading data into specific partitions
Loading data from local files into partitions p1 and p2 of the table, allowing a 20% error rate.
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "label:123" \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "max_filter_ratio:0.2" \
-H "column_separator:," \
-H "columns:user_id,name,age" \
-H "partitions: p1, p2" \
-T streamload_example.csv \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Loading data into specific timezone
DATETIME related types only represent absolute time points, do not contain time zone information, and will not change due to changes in the Doris system time zone. Therefore, for the import of data with time zones, our unified processing method is to convert it into data in a specific target time zone. In the Doris system, it is the time zone represented by the session variable time_zone.
In the import, our target time zone is specified through the parameter timezone. This variable will replace the session variable time_zone when time zone conversion occurs and time zone sensitive functions are calculated. Therefore, if there are no special circumstances, the timezone should be set in the import transaction to be consistent with the time_zone of the current Doris cluster. This means that all time data with a time zone will be converted to this time zone.
For example, the Doris system time zone is "+08:00", and the time column in the imported data contains two pieces of data, namely "2012-01-01 01:00:00+00:00" and "2015-12-12 12 :12:12-08:00", then after we specify the time zone of the imported transaction through -H "timezone: +08:00" when importing, both pieces of data will be converted to the time zone to obtain the result." 2012-01-01 09:00:00" and "2015-12-13 04:12:12".
For more information on time zone interpretation, please refer to the document Time Zone.
Streamingly import
Stream Load is based on the HTTP protocol for importing, which supports using programming languages such as Java, Go, or Python for streaming import. This is why it is named Stream Load.
The following example demonstrates this usage through a bash command pipeline. The imported data is generated streamingly by the program rather than from a local file.
seq 1 10 | awk '{OFS="\t"}{print $1, $1 * 10}' | curl --location-trusted -u root -T - http://host:port/api/testDb/testTbl/_stream_load
Set CSV first row filtering
File data:
id,name,age
1,doris,20
2,flink,10
Filtering the first row during load by specifying format=csv_with_names
curl --location-trusted -u root -T test.csv -H "label:1" -H "format:csv_with_names" -H "column_separator:," http://host:port/api/testDb/testTbl/_stream_load
Specifying merge_type for DELETE operations
In Stream Load, there are three import types: APPEND, DELETE, and MERGE. These can be adjusted by specifying the parameter merge_type. If you want to specify that all data with the same key as the imported data should be deleted, you can use the following command:
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "merge_type: DELETE" \
-H "column_separator:," \
-H "columns:user_id,name,age" \
-T streamload_example.csv \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Before loading:
+--------+----------+----------+------+
| siteid | citycode | username | pv |
+--------+----------+----------+------+
| 3 | 2 | tom | 2 |
| 4 | 3 | bush | 3 |
| 5 | 3 | helen | 3 |
+--------+----------+----------+------+
The imported data is:
3,2,tom,0
After importing, the original table data will be deleted, resulting in the following result:
+--------+----------+----------+------+
| siteid | citycode | username | pv |
+--------+----------+----------+------+
| 4 | 3 | bush | 3 |
| 5 | 3 | helen | 3 |
+--------+----------+----------+------+
Specifying merge_type for MERGE operation
By specifying merge_type as MERGE, the imported data can be merged into the table. The MERGE semantics need to be used in combination with the DELETE condition, which means that data satisfying the DELETE condition is processed according to the DELETE semantics, and the rest is added to the table according to the APPEND semantics. The following operation represents deleting the row with siteid of 1, and adding the rest of the data to the table:
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "merge_type: MERGE" \
-H "delete: siteid=1" \
-H "column_separator:," \
-H "columns:user_id,name,age" \
-T streamload_example.csv \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Before loading:
+--------+----------+----------+------+
| siteid | citycode | username | pv |
+--------+----------+----------+------+
| 4 | 3 | bush | 3 |
| 5 | 3 | helen | 3 |
| 1 | 1 | jim | 2 |
+--------+----------+----------+------+
The imported data is:
2,1,grace,2
3,2,tom,2
1,1,jim,2
After loading, the row with siteid = 1 will be deleted according to the condition, and the rows with siteid of 2 and 3 will be added to the table:
+--------+----------+----------+------+
| siteid | citycode | username | pv |
+--------+----------+----------+------+
| 4 | 3 | bush | 3 |
| 2 | 1 | grace | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | tom | 2 |
| 5 | 3 | helen | 3 |
+--------+----------+----------+------+
Specifying sequence column for merge
When a table with a Unique Key has a Sequence column, the value of the Sequence column serves as the basis for the replacement order in the REPLACE aggregation function under the same Key column. A larger value can replace a smaller one. When marking deletions based on DORIS_DELETE_SIGN for such a table, it is necessary to ensure that the Key is the same and that the Sequence column value is greater than or equal to the current value. By specifying the function_column.sequence_col parameter, deletion operations can be performed in combination with merge_type: DELETE.
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "merge_type: DELETE" \
-H "function_column.sequence_col: age" \
-H "column_separator:," \
-H "columns: name, gender, age"
-T streamload_example.csv \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Given the following table schema:
SET show_hidden_columns=true;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
DESC table1;
+------------------------+--------------+------+-------+---------+---------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+------------------------+--------------+------+-------+---------+---------+
| name | VARCHAR(100) | No | true | NULL | |
| gender | VARCHAR(10) | Yes | false | NULL | REPLACE |
| age | INT | Yes | false | NULL | REPLACE |
| __DORIS_DELETE_SIGN__ | TINYINT | No | false | 0 | REPLACE |
| __DORIS_SEQUENCE_COL__ | INT | Yes | false | NULL | REPLACE |
+------------------------+--------------+------+-------+---------+---------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
The original table data is:
+-------+--------+------+
| name | gender | age |
+-------+--------+------+
| li | male | 10 |
| wang | male | 14 |
| zhang | male | 12 |
+-------+--------+------+
-
Sequence parameter takes Eeffect, loading sequence column value is larger than or equal to the existing data in the table.
loading data as:
li,male,10
Since function_column.sequence_col is specified as age, and the age value is larger than or equal to the existing column in the table, the original table data is deleted. The table data becomes:
+-------+--------+------+
| name | gender | age |
+-------+--------+------+
| wang | male | 14 |
| zhang | male | 12 |
+-------+--------+------+
-
Sequence parameter do not take effect, loading sequence column value is less than or equal to the existing data in the table:
loading data as:
li,male,9
Since function_column.sequence_col is specified as age, but the age value is less than the existing column in the table, the delete operation does not take effect. The table data remains unchanged, and the row with the primary key of li is still visible:
+-------+--------+------+
| name | gender | age |
+-------+--------+------+
| li | male | 10 |
| wang | male | 14 |
| zhang | male | 12 |
+-------+--------+------+
It is not deleted because that, at the underlying dependency level, it first checks for rows with the same key. It displays the row data with the larger sequence column value. Then, it checks the DORIS_DELETE_SIGN value for that row. If it is 1, it is not displayed externally. If it is 0, it is still read and displayed.
Loading data with enclosing characters
When the data in a CSV file contains delimiters or separators, single-byte characters can be specified as enclosing characters to protect the data from being truncated.
For example, in the following data where a comma is used as the separator but also exists within a field:
zhangsan,30,'Shanghai, HuangPu District, Dagu Road'
By specifying an enclosing character such as a single quotation mark ', the entire Shanghai, HuangPu District, Dagu Road can be treated as a single field.
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "column_separator:," \
-H "enclose:'" \
-H "columns:username,age,address" \
-T streamload_example.csv \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
If the enclosing character also appears within a field, such as wanting to treat Shanghai City, Huangpu District, \'Dagu Road as a single field, it is necessary to first perform string escaping within the column:
Zhang San,30,'Shanghai, Huangpu District, \'Dagu Road'
An escape character, which is a single-byte character, can be specified using the escape parameter. In the example, the backslash \ is used as the escape character.
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "column_separator:," \
-H "enclose:'" \
-H "escape:\\" \
-H "columns:username,age,address" \
-T streamload_example.csv \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Loading fields containing default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP type
Here's an example of loading data into a table that contains a field with the DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP type:
Table schema:
`id` bigint(30) NOT NULL,
`order_code` varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '',
`create_time` datetimev2(3) DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
JSON data type:
{"id":1,"order_Code":"avc"}
Command:
curl --location-trusted -u root -T test.json -H "label:1" -H "format:json" -H 'columns: id, order_code, create_time=CURRENT_TIMESTAMP()' http://host:port/api/testDb/testTbl/_stream_load
Simple mode for loading JSON format data
When the JSON fields correspond one-to-one with the column names in the table, you can import JSON data format into the table by specifying the parameters "strip_outer_array:true" and "format:json".
For example, if the table is defined as follows:
CREATE TABLE testdb.test_streamload(
user_id BIGINT NOT NULL COMMENT "User ID",
name VARCHAR(20) COMMENT "User name",
age INT COMMENT "User age"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(user_id)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(user_id) BUCKETS 10;
And the data field names correspond one-to-one with the column names in the table:
[
{"user_id":1,"name":"Emily","age":25},
{"user_id":2,"name":"Benjamin","age":35},
{"user_id":3,"name":"Olivia","age":28},
{"user_id":4,"name":"Alexander","age":60},
{"user_id":5,"name":"Ava","age":17},
{"user_id":6,"name":"William","age":69},
{"user_id":7,"name":"Sophia","age":32},
{"user_id":8,"name":"James","age":64},
{"user_id":9,"name":"Emma","age":37},
{"user_id":10,"name":"Liam","age":64}
]
You can use the following command to load JSON data into the table:
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "format:json" \
-H "strip_outer_array:true" \
-T streamload_example.json \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Matching mode for loading complex JSON format data
When the JSON data is more complex and cannot correspond one-to-one with the column names in the table, or there are extra columns, you can use the jsonpaths parameter to complete the column name mapping and perform data matching import. For example, with the following data:
[
{"userid":1,"hudi":"lala","username":"Emily","userage":25,"userhp":101},
{"userid":2,"hudi":"kpkp","username":"Benjamin","userage":35,"userhp":102},
{"userid":3,"hudi":"ji","username":"Olivia","userage":28,"userhp":103},
{"userid":4,"hudi":"popo","username":"Alexander","userage":60,"userhp":103},
{"userid":5,"hudi":"uio","username":"Ava","userage":17,"userhp":104},
{"userid":6,"hudi":"lkj","username":"William","userage":69,"userhp":105},
{"userid":7,"hudi":"komf","username":"Sophia","userage":32,"userhp":106},
{"userid":8,"hudi":"mki","username":"James","userage":64,"userhp":107},
{"userid":9,"hudi":"hjk","username":"Emma","userage":37,"userhp":108},
{"userid":10,"hudi":"hua","username":"Liam","userage":64,"userhp":109}
]
You can specify the jsonpaths parameter to match the specified columns:
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "format:json" \
-H "strip_outer_array:true" \
-H "jsonpaths:[\"$.userid\", \"$.username\", \"$.userage\"]" \
-H "columns:user_id,name,age" \
-T streamload_example.json \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Specifying JSON root node for data load
If the JSON data contains nested JSON fields, you need to specify the root node of the imported JSON. The default value is "".
For example, with the following data, if you want to import the data in the comment column into the table:
[
{"user":1,"comment":{"userid":101,"username":"Emily","userage":25}},
{"user":2,"comment":{"userid":102,"username":"Benjamin","userage":35}},
{"user":3,"comment":{"userid":103,"username":"Olivia","userage":28}},
{"user":4,"comment":{"userid":104,"username":"Alexander","userage":60}},
{"user":5,"comment":{"userid":105,"username":"Ava","userage":17}},
{"user":6,"comment":{"userid":106,"username":"William","userage":69}},
{"user":7,"comment":{"userid":107,"username":"Sophia","userage":32}},
{"user":8,"comment":{"userid":108,"username":"James","userage":64}},
{"user":9,"comment":{"userid":109,"username":"Emma","userage":37}},
{"user":10,"comment":{"userid":110,"username":"Liam","userage":64}}
]
First, you need to specify the root node as comment using the json_root parameter, and then complete the column name mapping according to the jsonpaths parameter.
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "format:json" \
-H "strip_outer_array:true" \
-H "json_root: $.comment" \
-H "jsonpaths:[\"$.userid\", \"$.username\", \"$.userage\"]" \
-H "columns:user_id,name,age" \
-T streamload_example.json \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Loading array data type
For example, if the following data contains an array type:
1|Emily|[1,2,3,4]
2|Benjamin|[22,45,90,12]
3|Olivia|[23,16,19,16]
4|Alexander|[123,234,456]
5|Ava|[12,15,789]
6|William|[57,68,97]
7|Sophia|[46,47,49]
8|James|[110,127,128]
9|Emma|[19,18,123,446]
10|Liam|[89,87,96,12]
Load data into the following table structure:
CREATE TABLE testdb.test_streamload(
typ_id BIGINT NOT NULL COMMENT "ID",
name VARCHAR(20) NULL COMMENT "Name",
arr ARRAY<int(10)> NULL COMMENT "Array"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(typ_id)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(typ_id) BUCKETS 10;
You can directly load the ARRAY type from a text file into the table using a Stream Load job.
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "column_separator:|" \
-H "columns:typ_id,name,arr" \
-T streamload_example.csv \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Loading map data type
When the imported data contains a map type, as in the following example:
[
{"user_id":1,"namemap":{"Emily":101,"age":25}},
{"user_id":2,"namemap":{"Benjamin":102,"age":35}},
{"user_id":3,"namemap":{"Olivia":103,"age":28}},
{"user_id":4,"namemap":{"Alexander":104,"age":60}},
{"user_id":5,"namemap":{"Ava":105,"age":17}},
{"user_id":6,"namemap":{"William":106,"age":69}},
{"user_id":7,"namemap":{"Sophia":107,"age":32}},
{"user_id":8,"namemap":{"James":108,"age":64}},
{"user_id":9,"namemap":{"Emma":109,"age":37}},
{"user_id":10,"namemap":{"Liam":110,"age":64}}
]
Load data into the following table structure:
CREATE TABLE testdb.test_streamload(
user_id BIGINT NOT NULL COMMENT "ID",
namemap Map<STRING, INT> NULL COMMENT "Name"
)
DUPLICATE KEY(user_id)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(user_id) BUCKETS 10;
You can directly load the map type from a text file into the table using a Stream Load task.
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "format: json" \
-H "strip_outer_array:true" \
-T streamload_example.json \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Loading bitmap data type
During the import process, when encountering Bitmap type data, you can use to_bitmap to convert the data into Bitmap, or use the bitmap_empty function to fill the Bitmap.
For example, with the following data:
1|koga|17723
2|nijg|146285
3|lojn|347890
4|lofn|489871
5|jfin|545679
6|kon|676724
7|nhga|767689
8|nfubg|879878
9|huang|969798
10|buag|97997
Load data into the following table containing the Bitmap type:
CREATE TABLE testdb.test_streamload(
typ_id BIGINT NULL COMMENT "ID",
hou VARCHAR(10) NULL COMMENT "one",
arr BITMAP BITMAP_UNION NOT NULL COMMENT "two"
)
AGGREGATE KEY(typ_id,hou)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(typ_id,hou) BUCKETS 10;
And use to_bitmap to convert the data into the Bitmap type.
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "Expect:100-continue" \
-H "columns:typ_id,hou,arr,arr=to_bitmap(arr)" \
-T streamload_example.csv \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Loading HyperLogLog data type
You can use the hll_hash function to convert data into the hll type, as in the following example:
1001|koga
1002|nijg
1003|lojn
1004|lofn
1005|jfin
1006|kon
1007|nhga
1008|nfubg
1009|huang
1010|buag
Load data into the following table:
CREATE TABLE testdb.test_streamload(
typ_id BIGINT NULL COMMENT "ID",
typ_name VARCHAR(10) NULL COMMENT "NAME",
pv hll hll_union NOT NULL COMMENT "hll"
)
AGGREGATE KEY(typ_id,typ_name)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(typ_id) BUCKETS 10;
And use the hll_hash command for import.
curl --location-trusted -u <doris_user>:<doris_password> \
-H "column_separator:|" \
-H "columns:typ_id,typ_name,pv=hll_hash(typ_id)" \
-T streamload_example.csv \
-XPUT http://<fe_ip>:<fe_http_port>/api/testdb/test_streamload/_stream_load
Column mapping, derived columns, and filtering
Doris supports a very rich set of column transformations and filtering operations in load statements. Supports most built-in functions. For how to use this feature correctly, please refer to the Data Transformation documentation.
Enable strict mode import
The strict_mode attribute is used to set whether the import task runs in strict mode. This attribute affects the results of column mapping, transformation, and filtering. For specific instructions on strict mode, please refer to the Handling Messy Data documentation.
Perform partial column updates/flexible partial update during import
For how to express partial column updates during import, please refer to the Partial Column Update documentation.
